SQL Always On
SQL Always On is a high-availability and disaster recovery solution in Microsoft SQL Server. It provides redundancy and failover capabilities for SQL databases, ensuring they remain accessible even in the event of hardware or software failures.
Topology
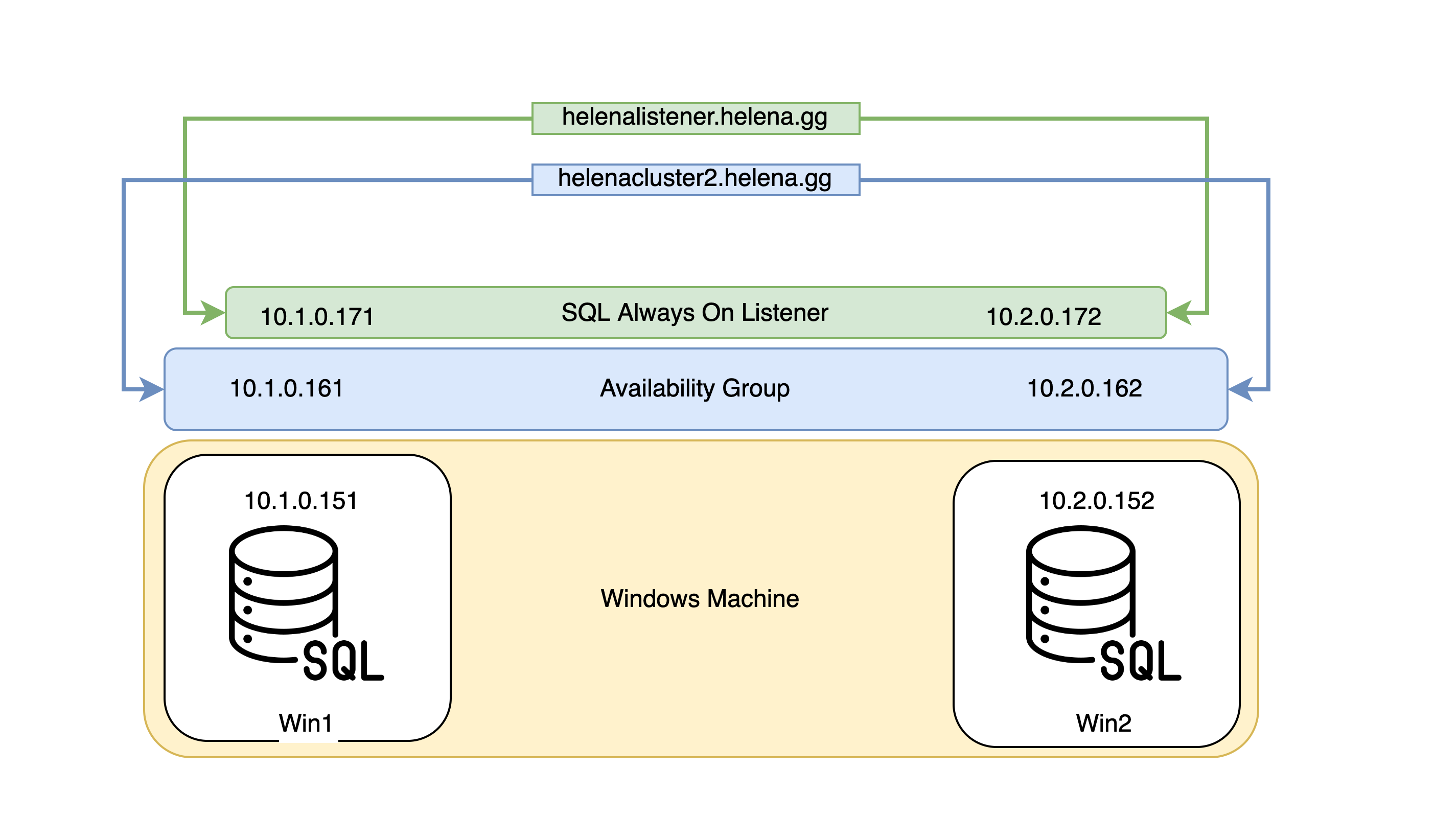
Here’s this deployment topology, where there will be 2 Windows Servers with SQL Server on Win1 and Win2, and we’ll create a load balancing Windows Availabilty Group Failover Cluster and also a load balancing SQL Always On Listener. These FQDNs will determine which IP Address is used based on their availability
Configuring Windows Failover Cluster
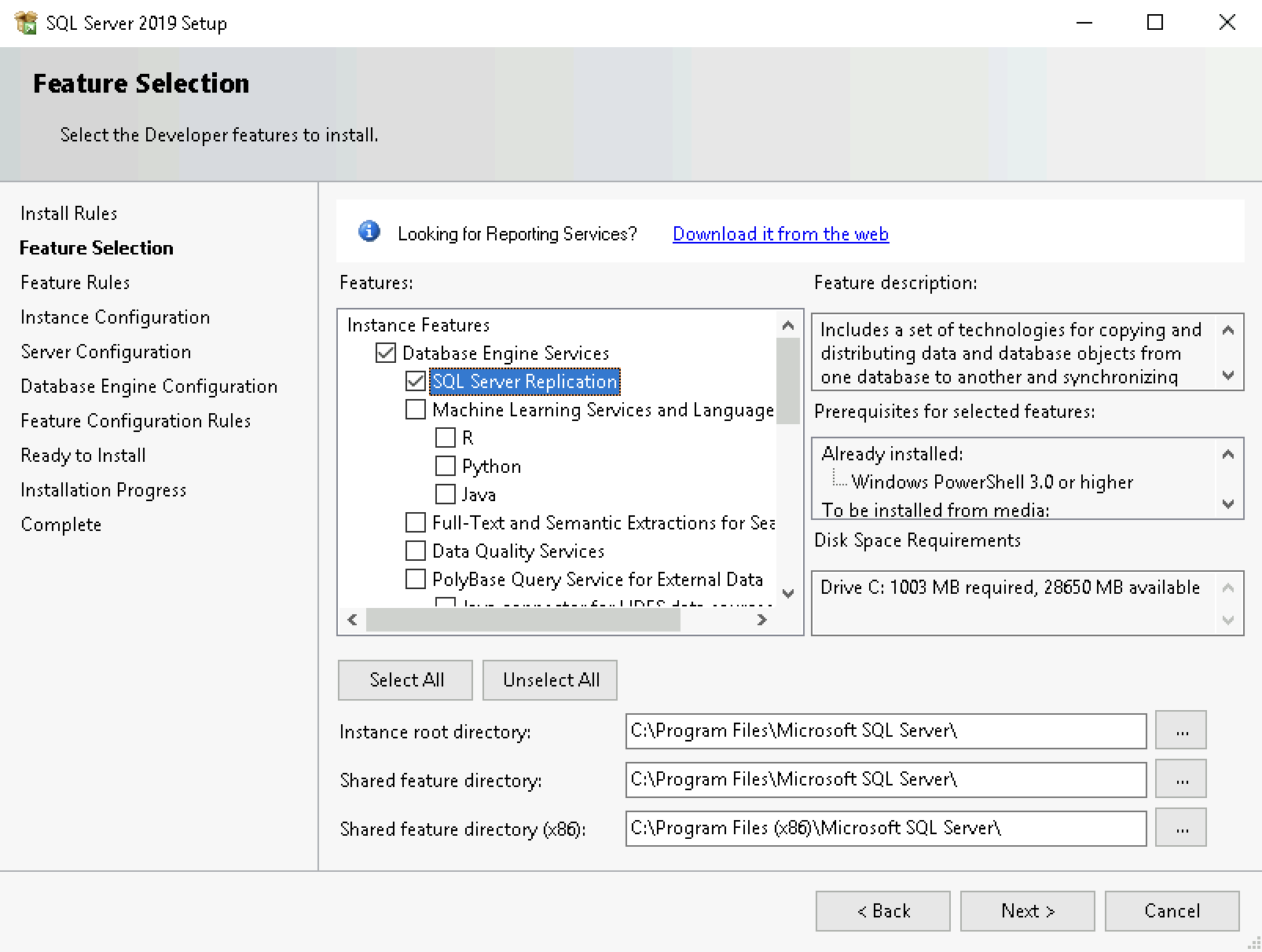
When installing SQL Server, make sure to also install the SQL Server Replication Feature
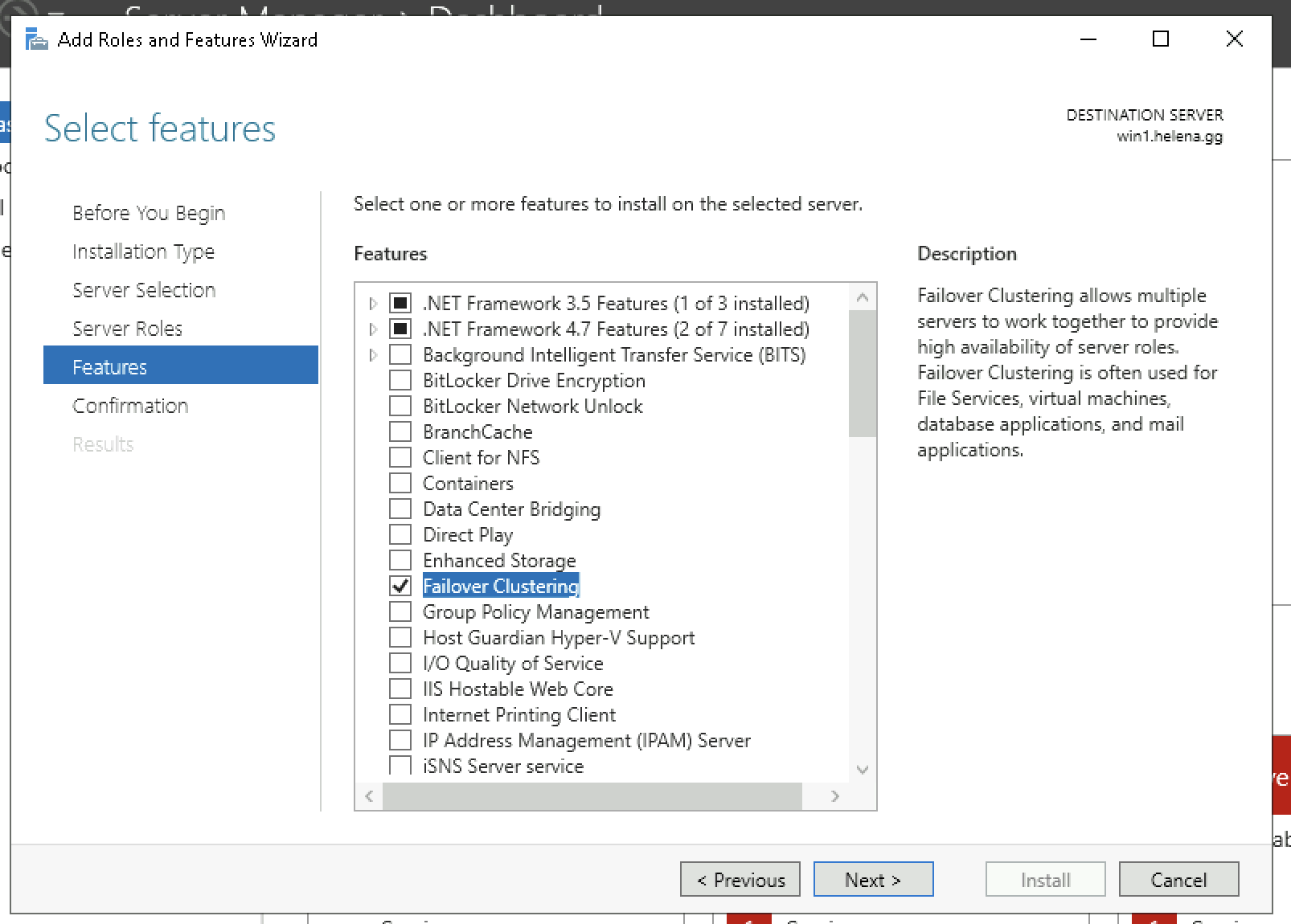
Then add the Failover Clustering on the Windows Server Manager on both servers
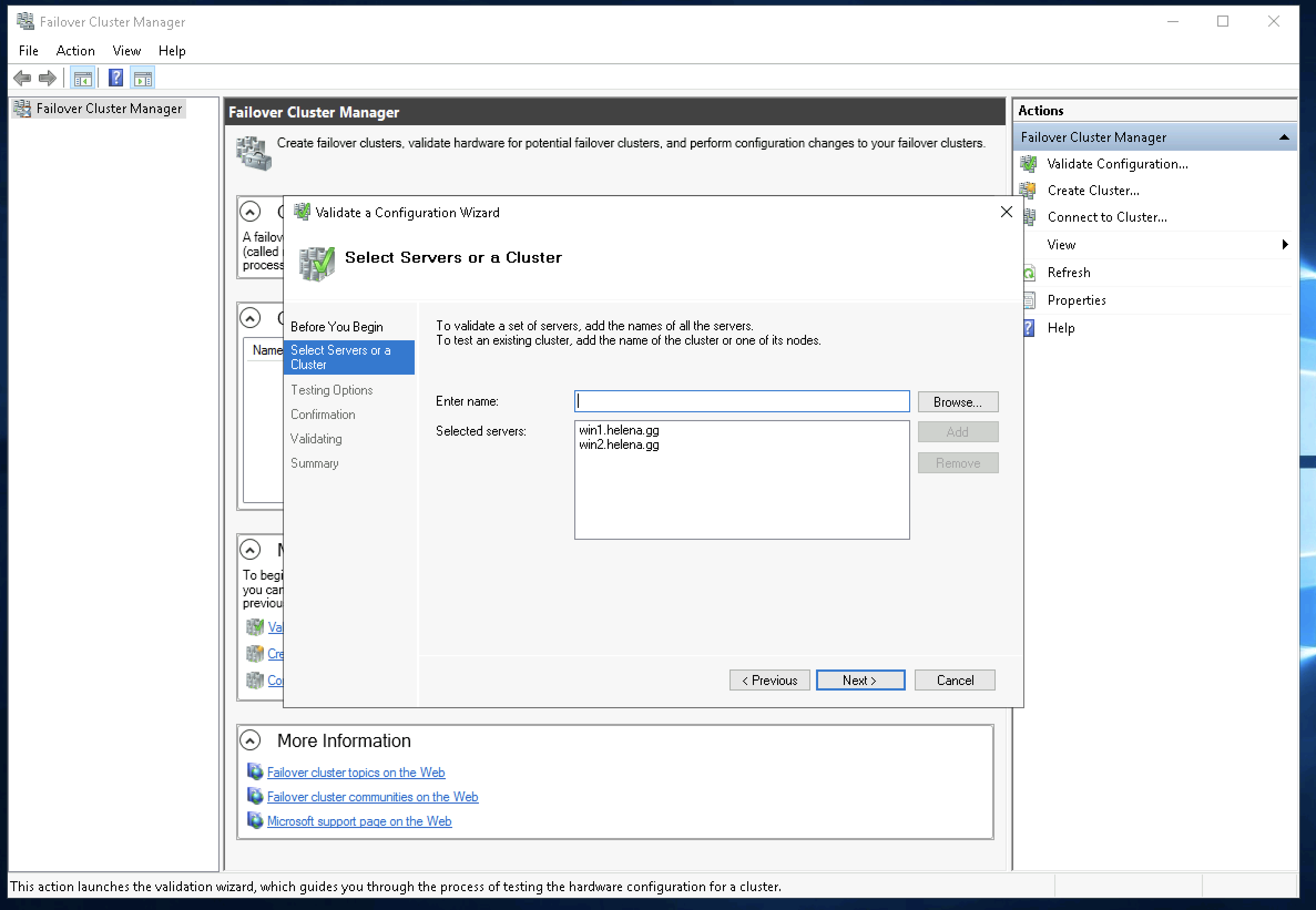
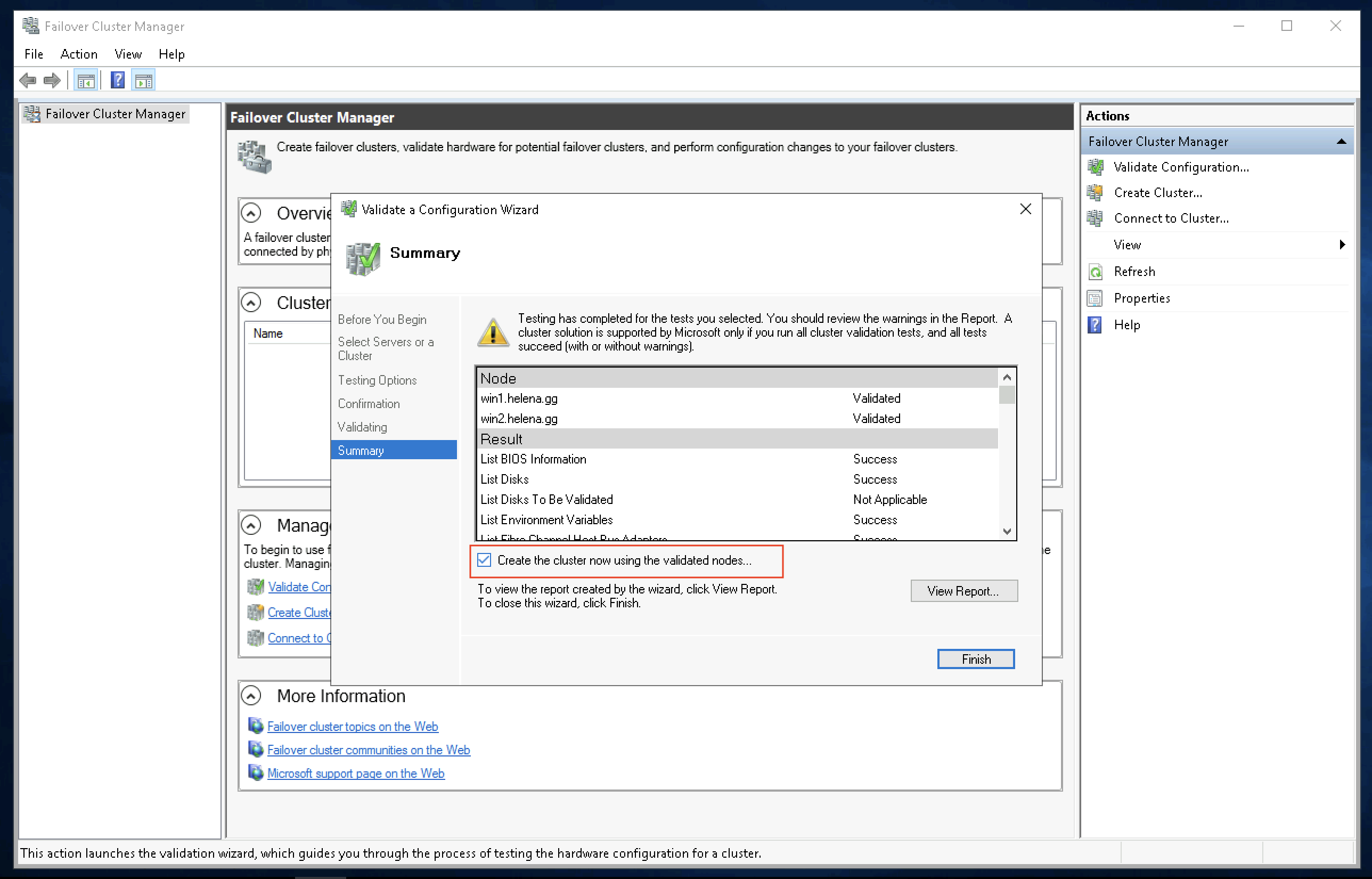
After that, on one of the server open Failover Cluster Manager, select Validate Configuration, and add the 2 servers
After the process finishes, check on “Create the cluster now … “ and select finish
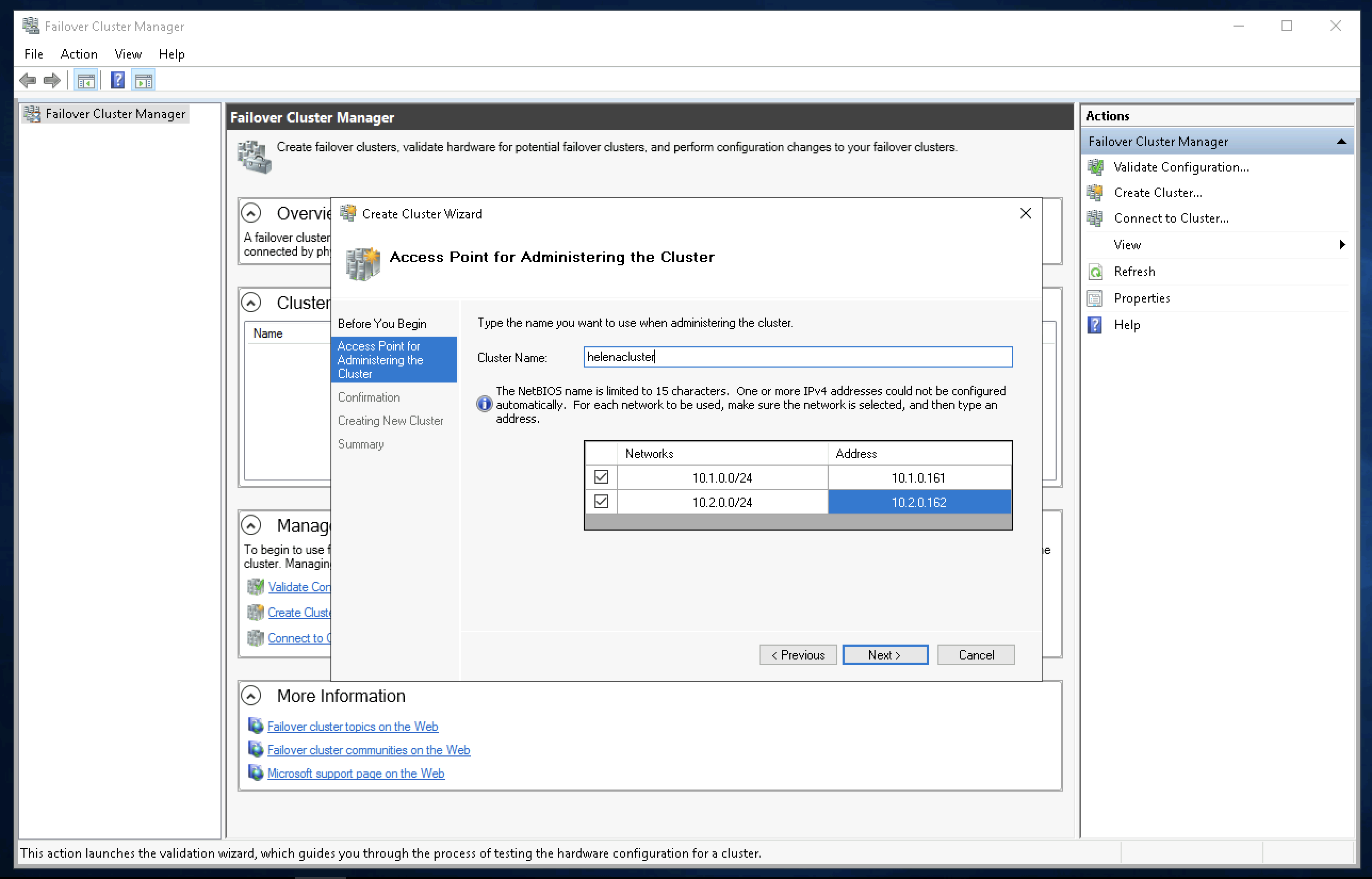
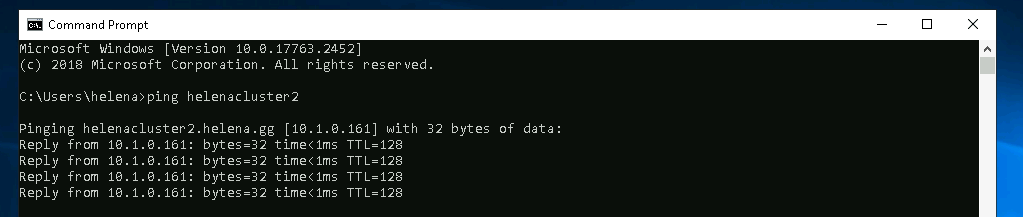
Now create the cluster name of “helenacluster2” and give each of them an IP Address
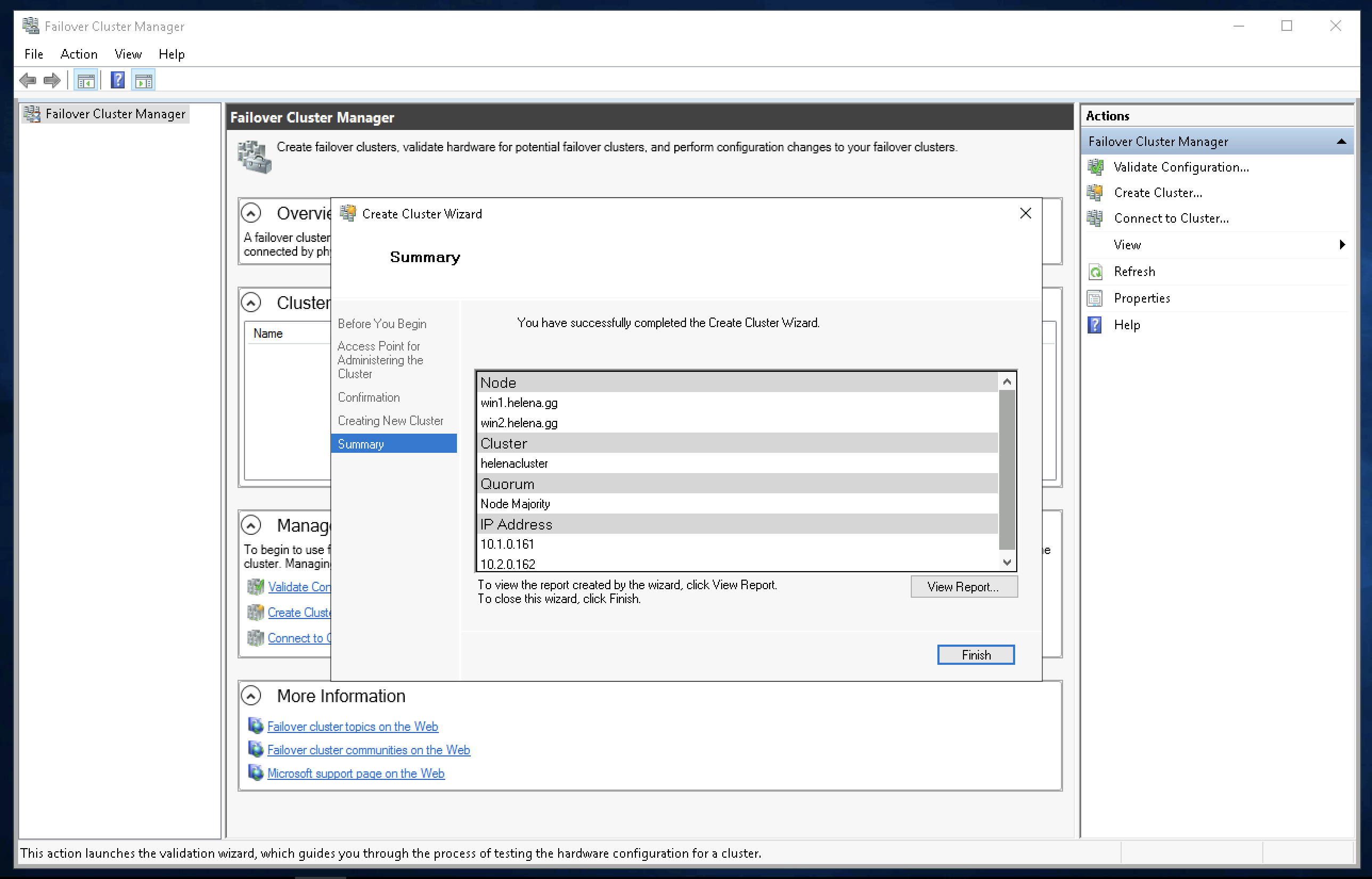
Review the summary and choose finish
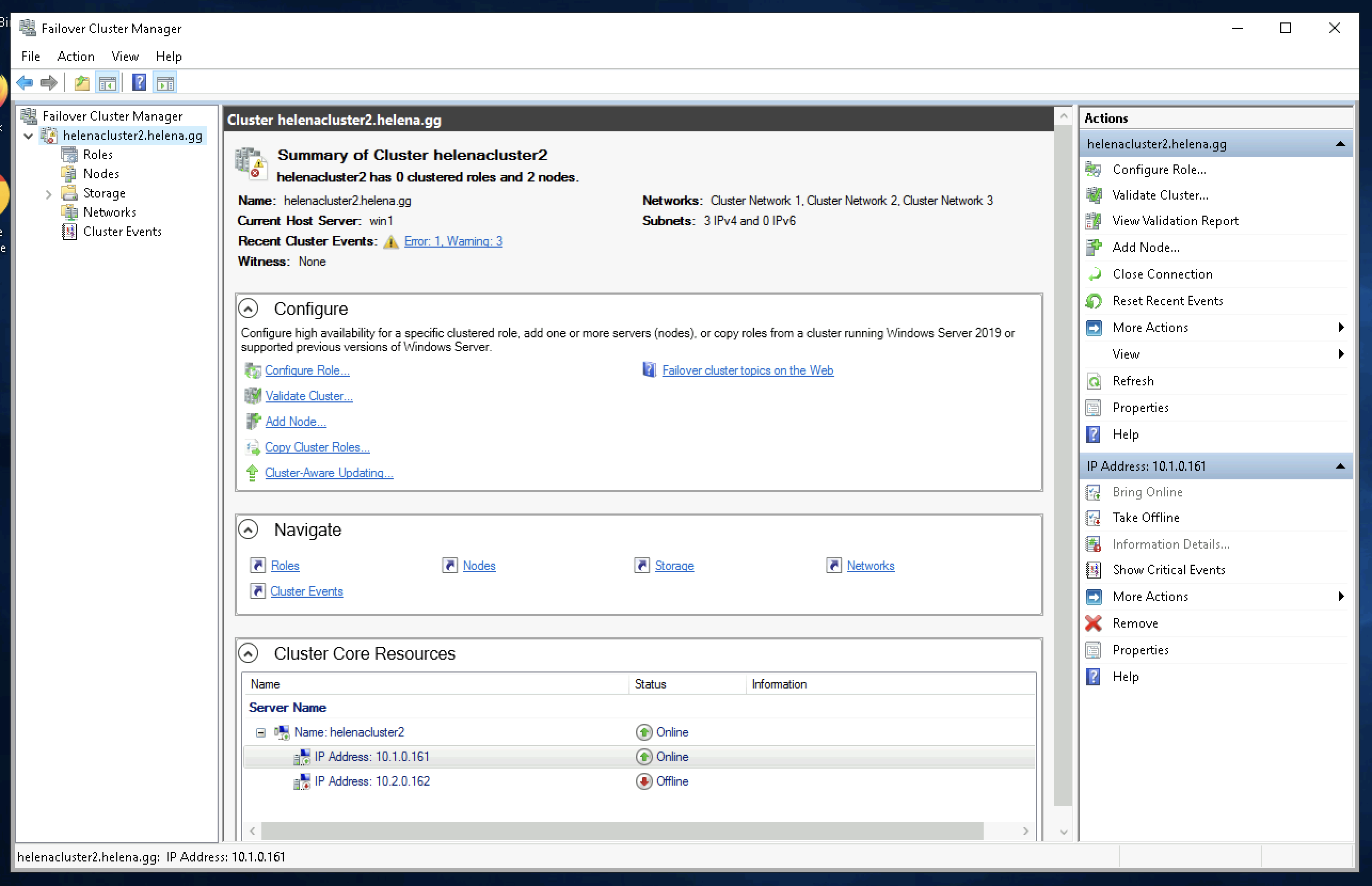
Now the failover cluster is up, and the active node is on Win1
And if we ping the helenacluster2, we should get a return IP Address of the currently active node
Configuring SQL Always On
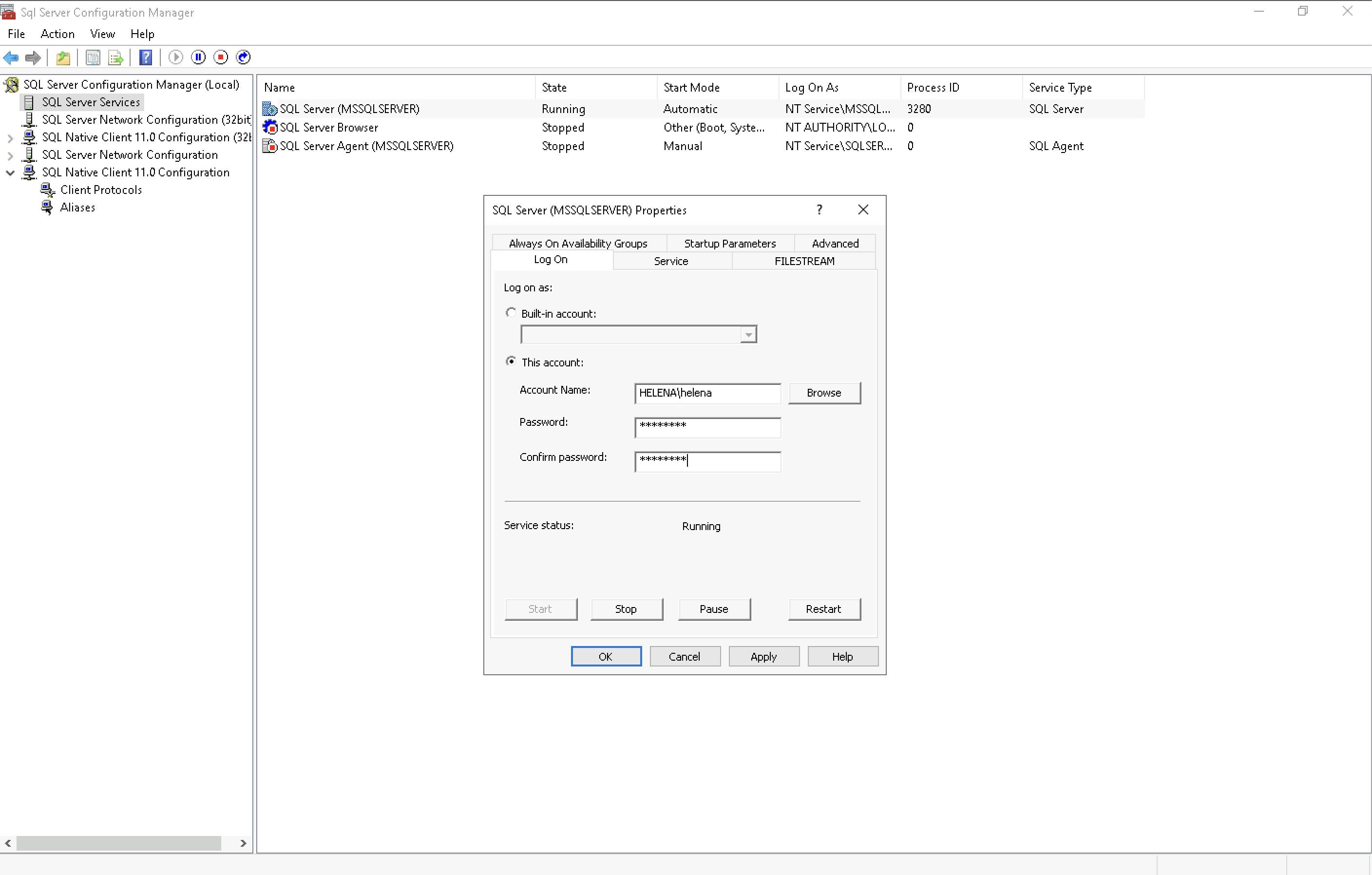
On SQL Server Configuration Manager, Open the SQL Server Service and change the user to the domain user
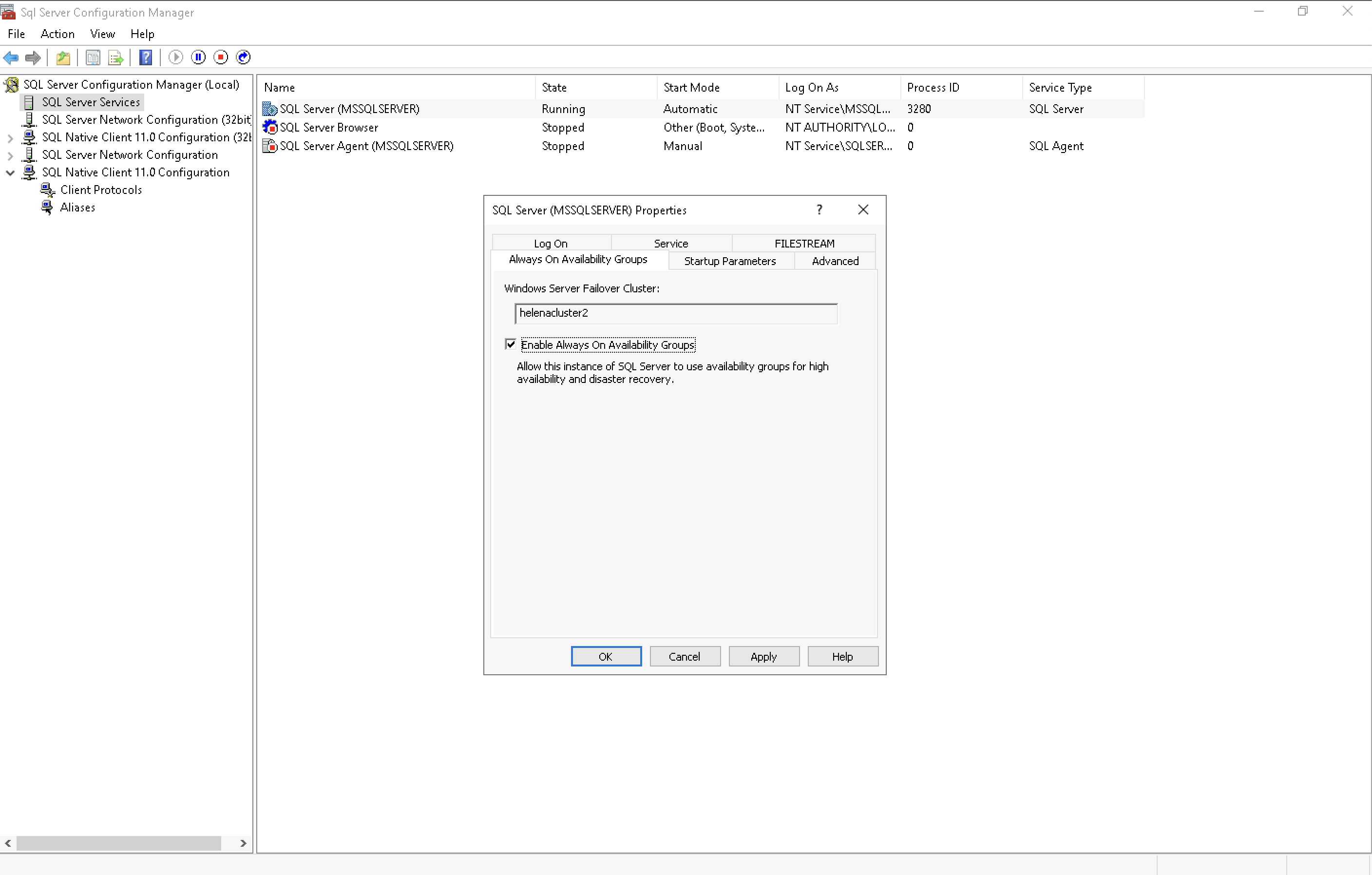
And on Always On Availability Group, select Enable
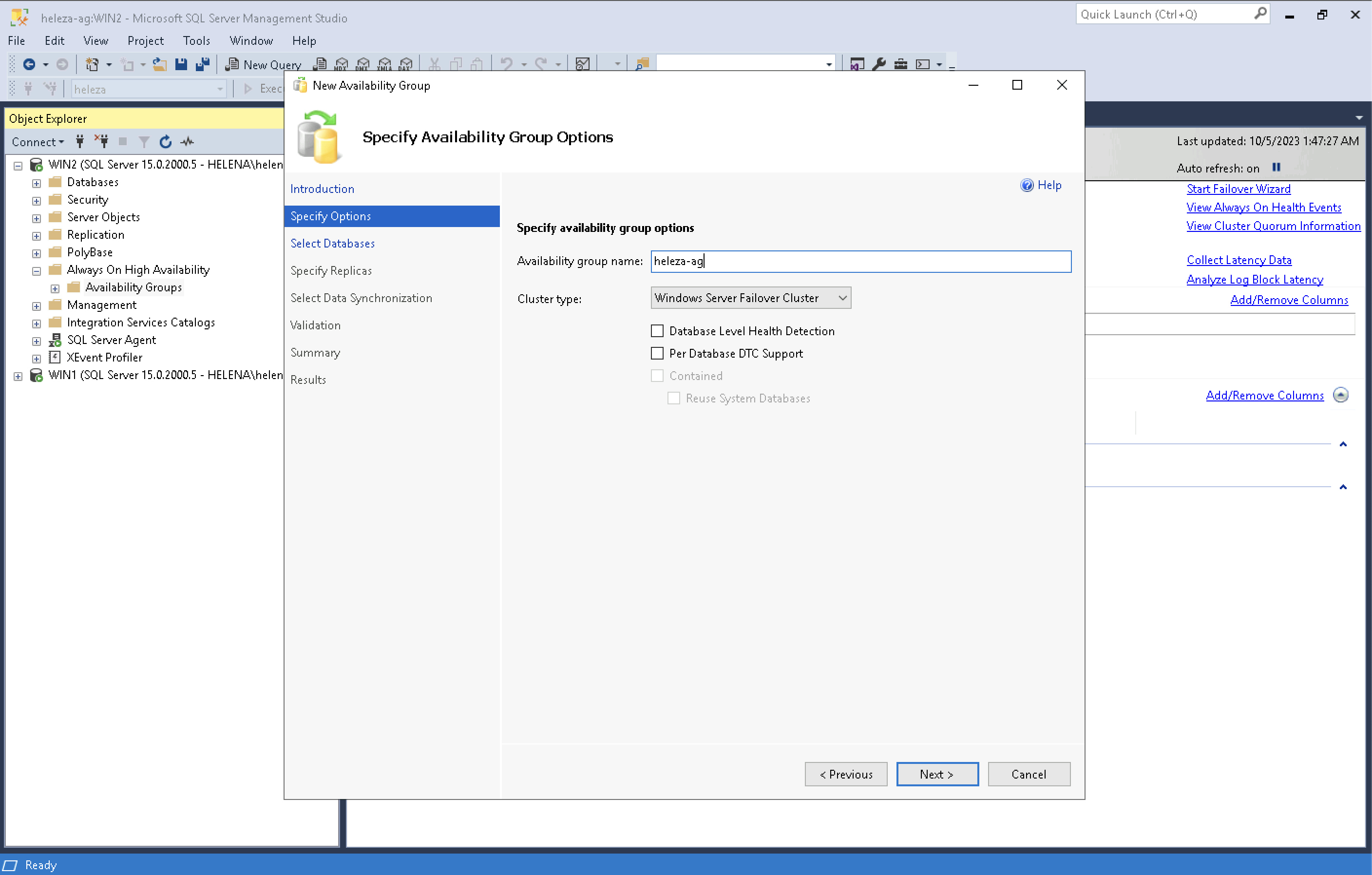
Now open SSMS, on Alway On Availabilty Groups, right click and add new
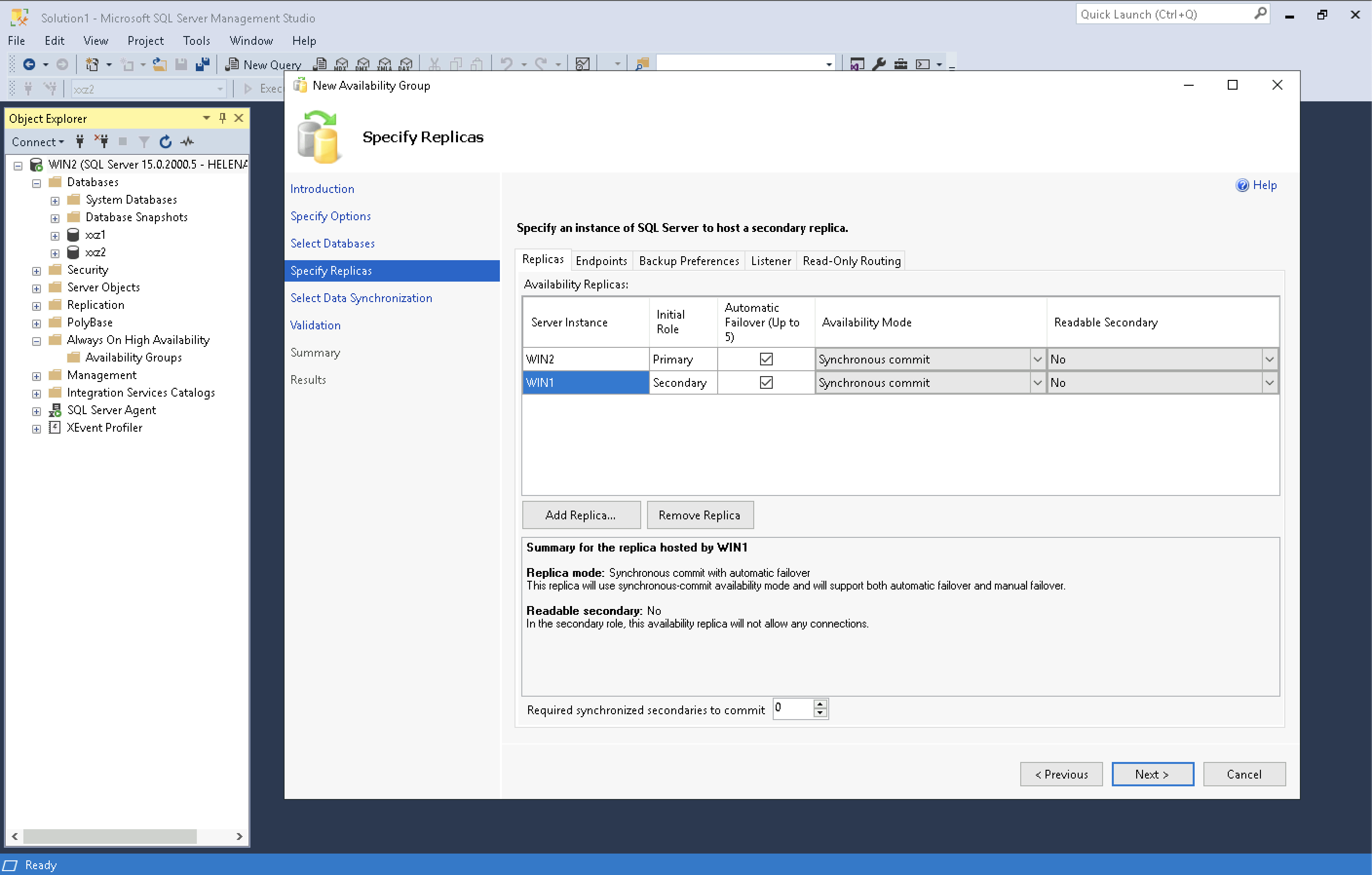
Select the Database and the Primary and Secondary Replica Servers
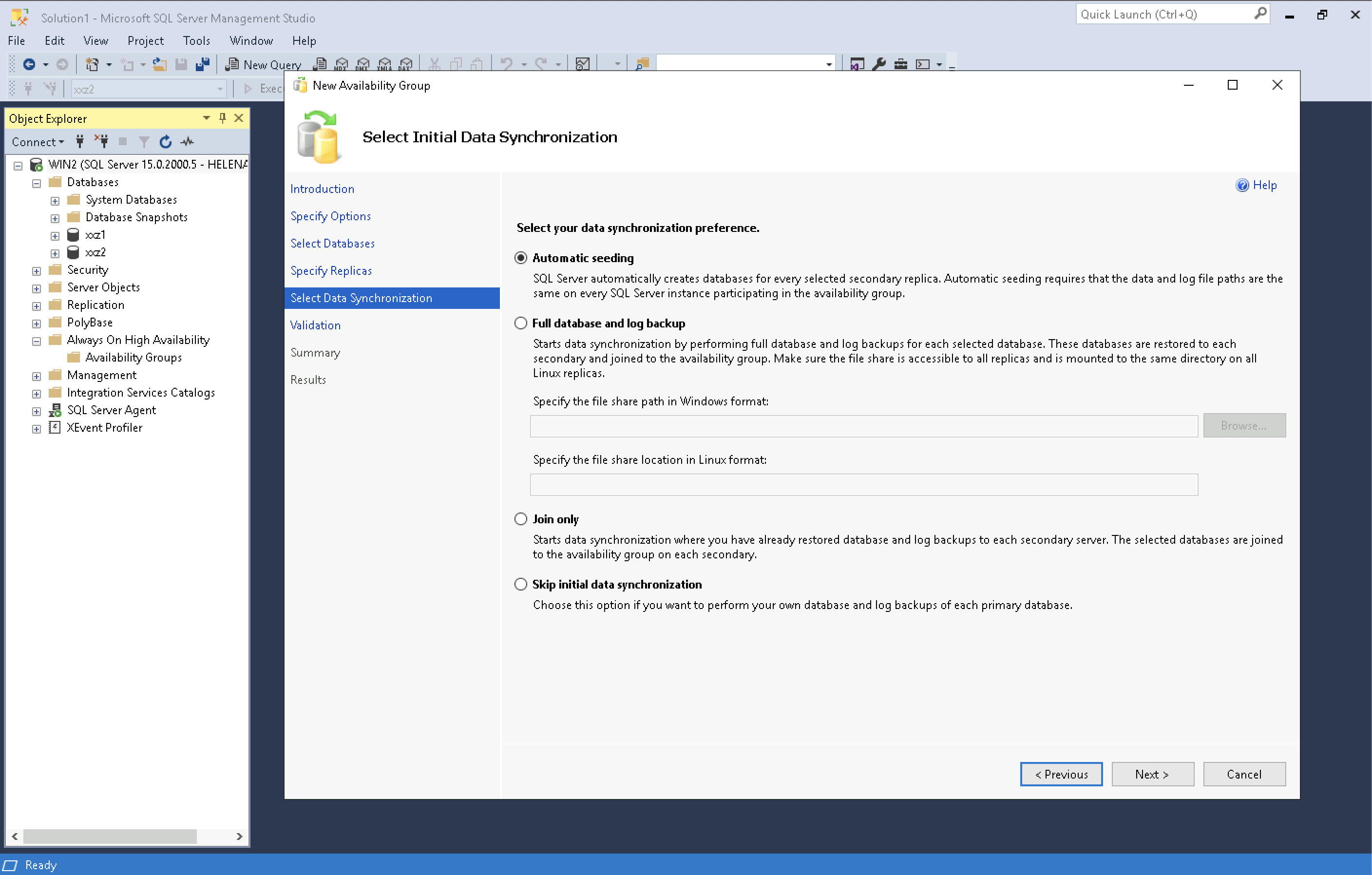
Then select the data synchronization type
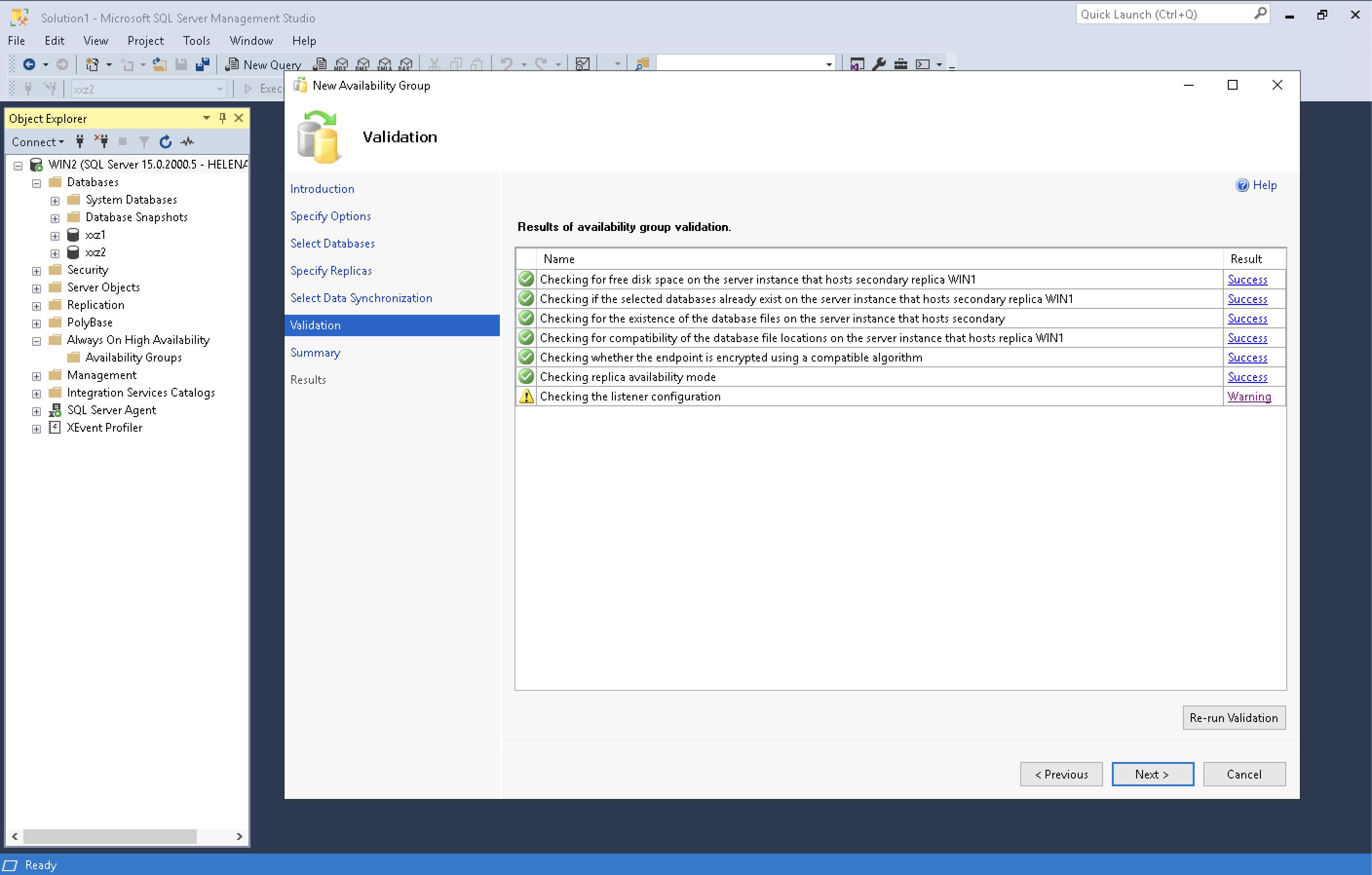
Run the validation, the listener will have a warning because we haven’t set it up yet, then select next until finish
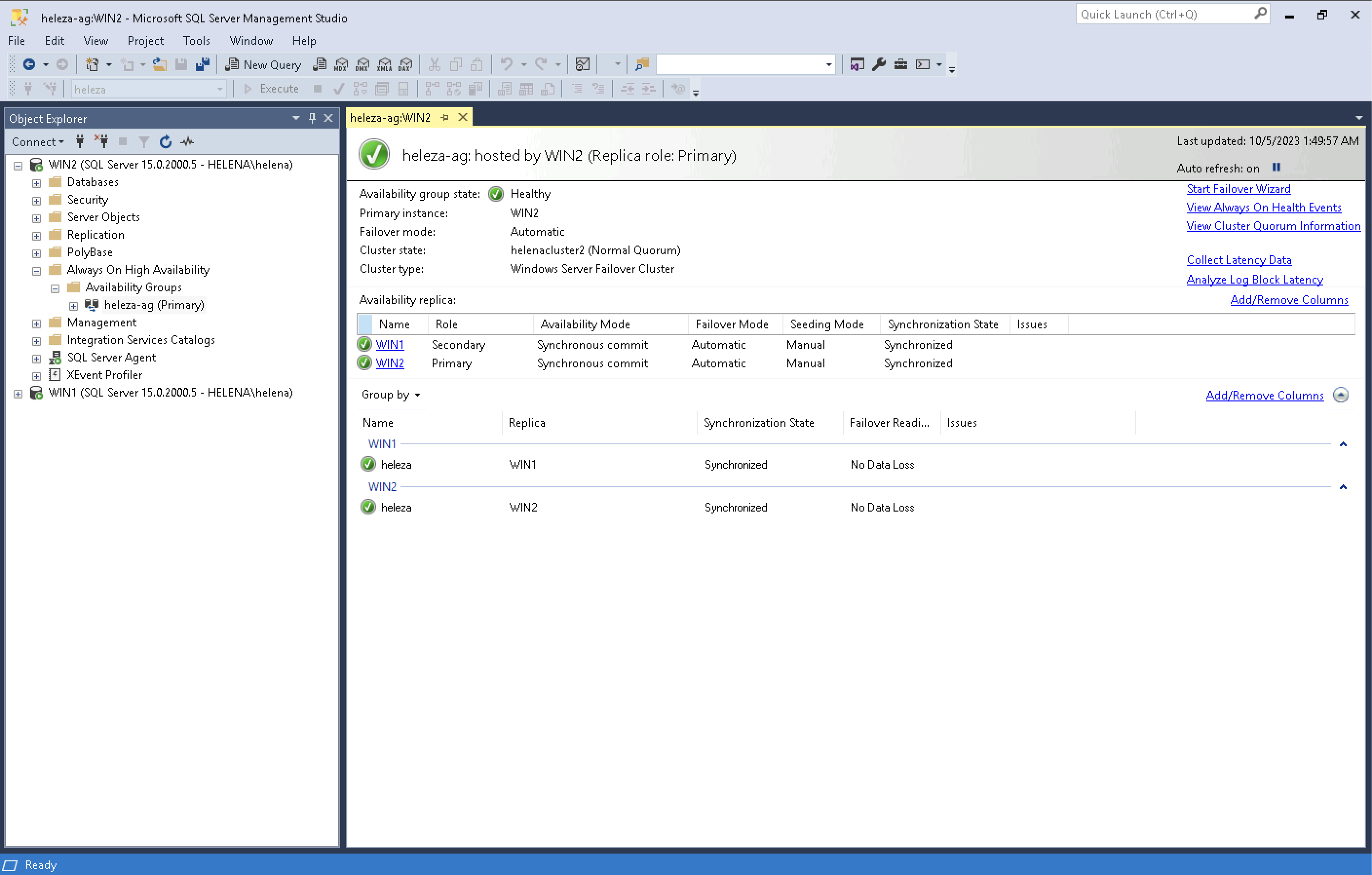
Now the Always On Availabilty Group is up, it’ll take sometime for the entire database being synced from the primary to the secondary replica
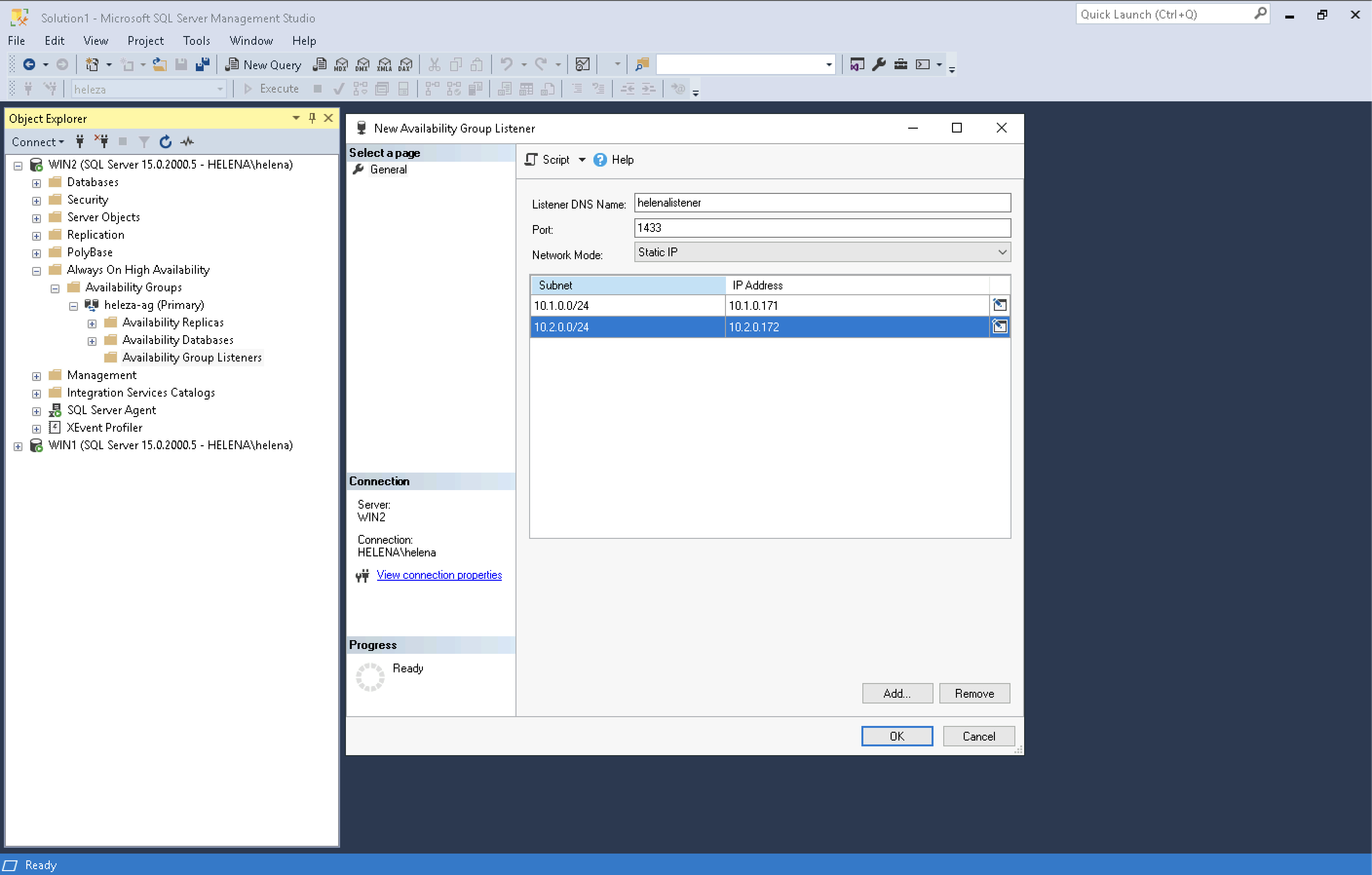
Now we set up the listener, on the availabilty group that’s been made, right click on Availabilty Group Listeners and add new.
Give it a name and IP Addresses
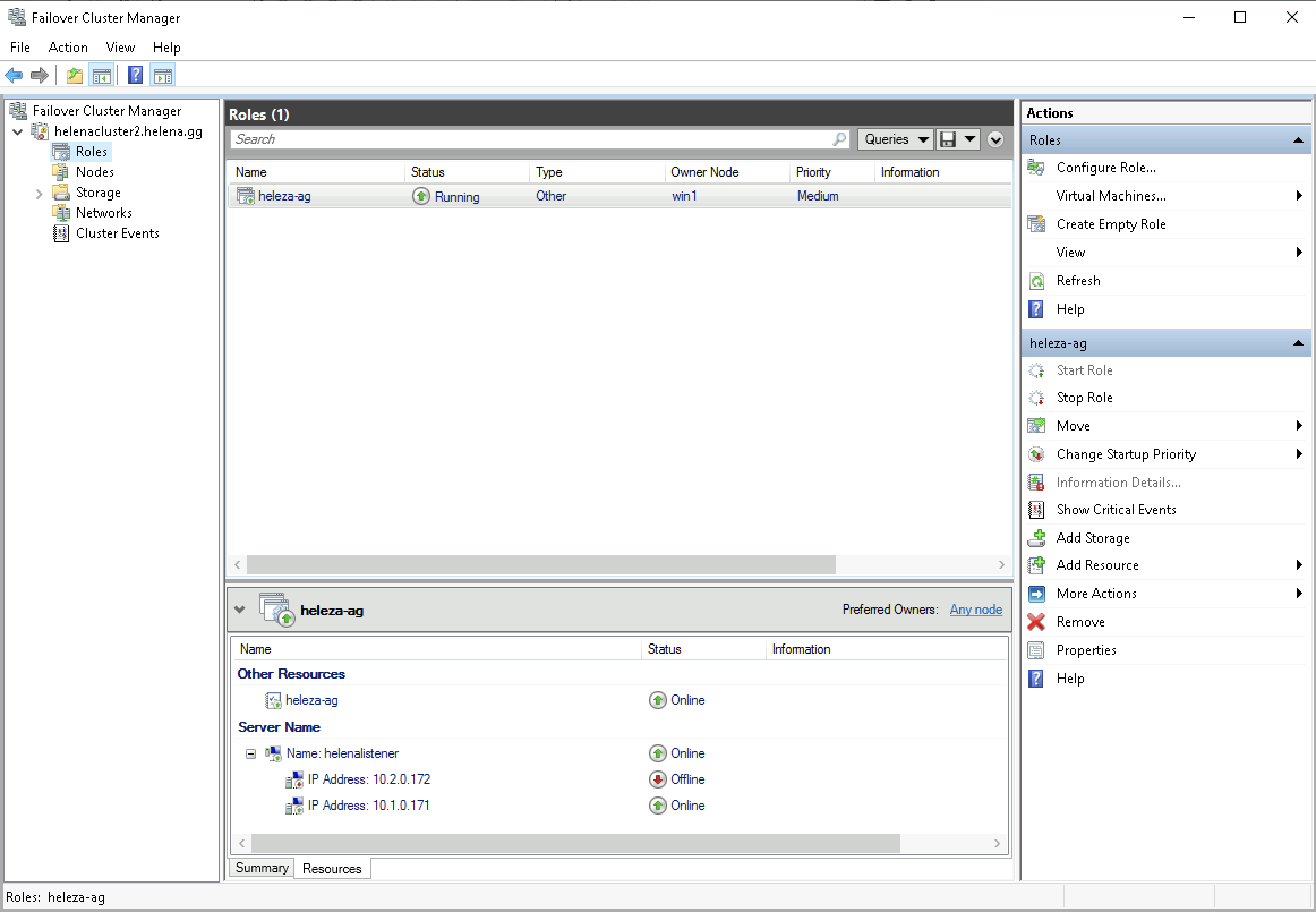
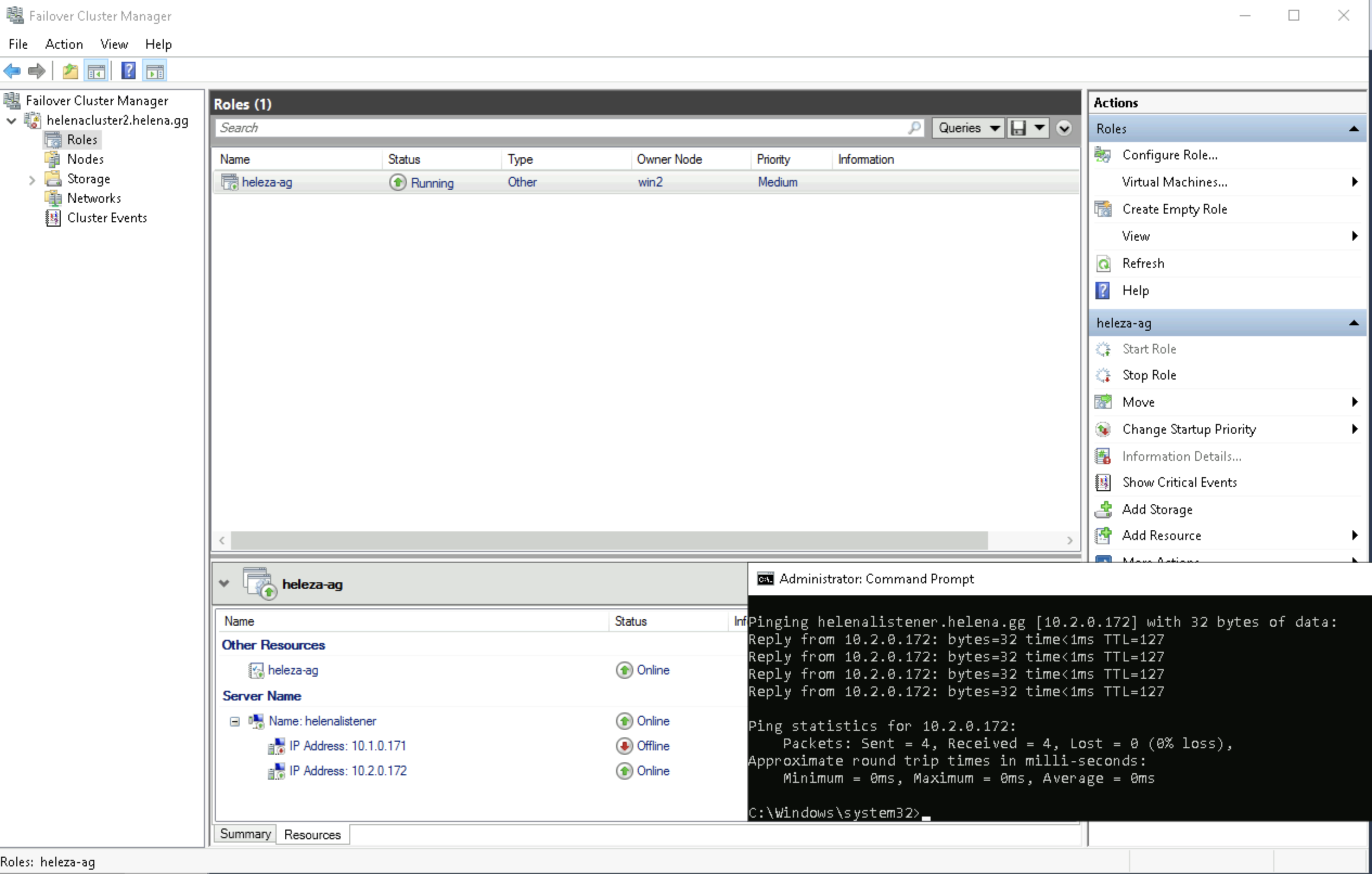
And thats about it. Now if we open the Failover Cluster Manager, we should see the SQL Always On Availablity Group on the roles tab
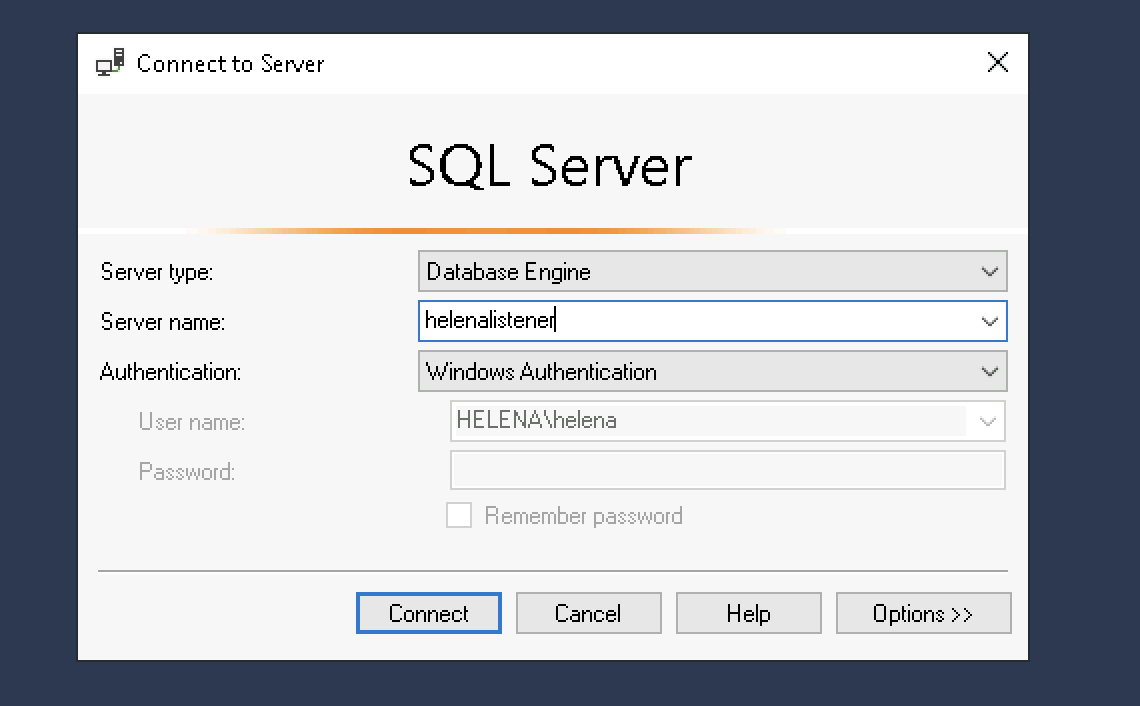
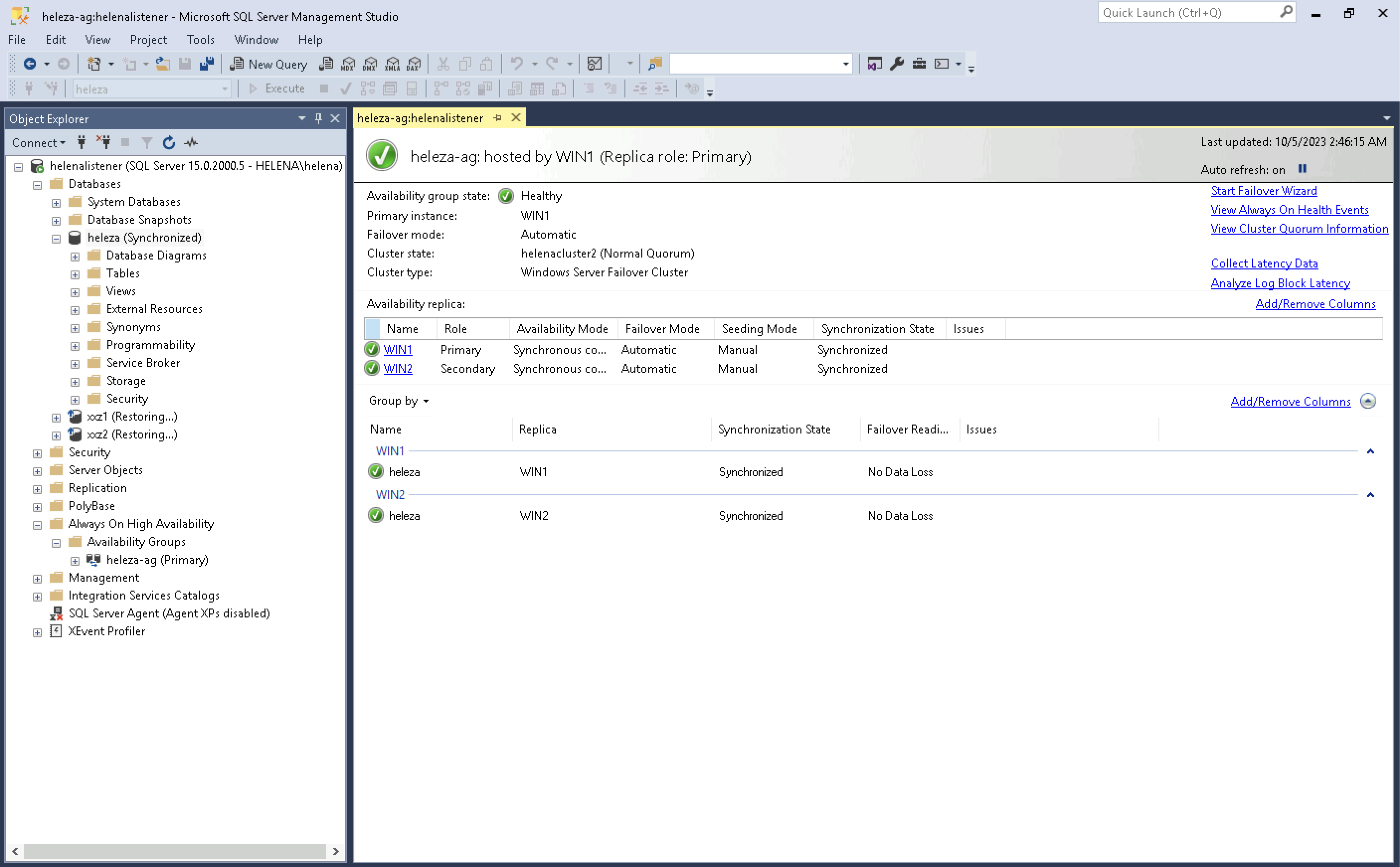
And connecting to the database using the listener also works. This listener will automatically return the IP Address of the active database
Testing Failover of SQL Always On
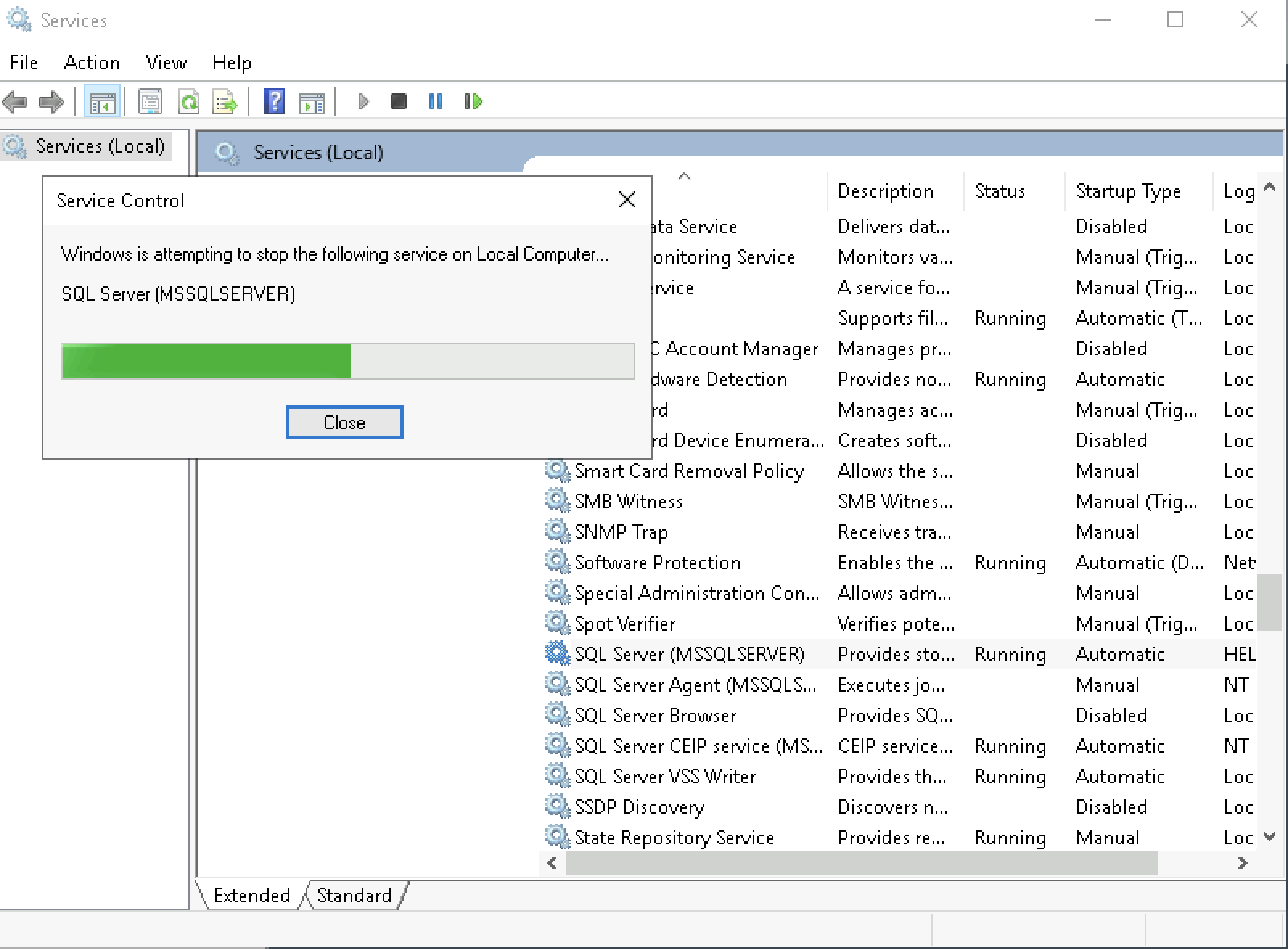
Now let’s try stopping the SQL Service on Win1, this will trigger the listener to go to the next available node, which is the Win2
As we can see here, the active node now is Win2 and pinging helenalistener returns the IP Address of Win2
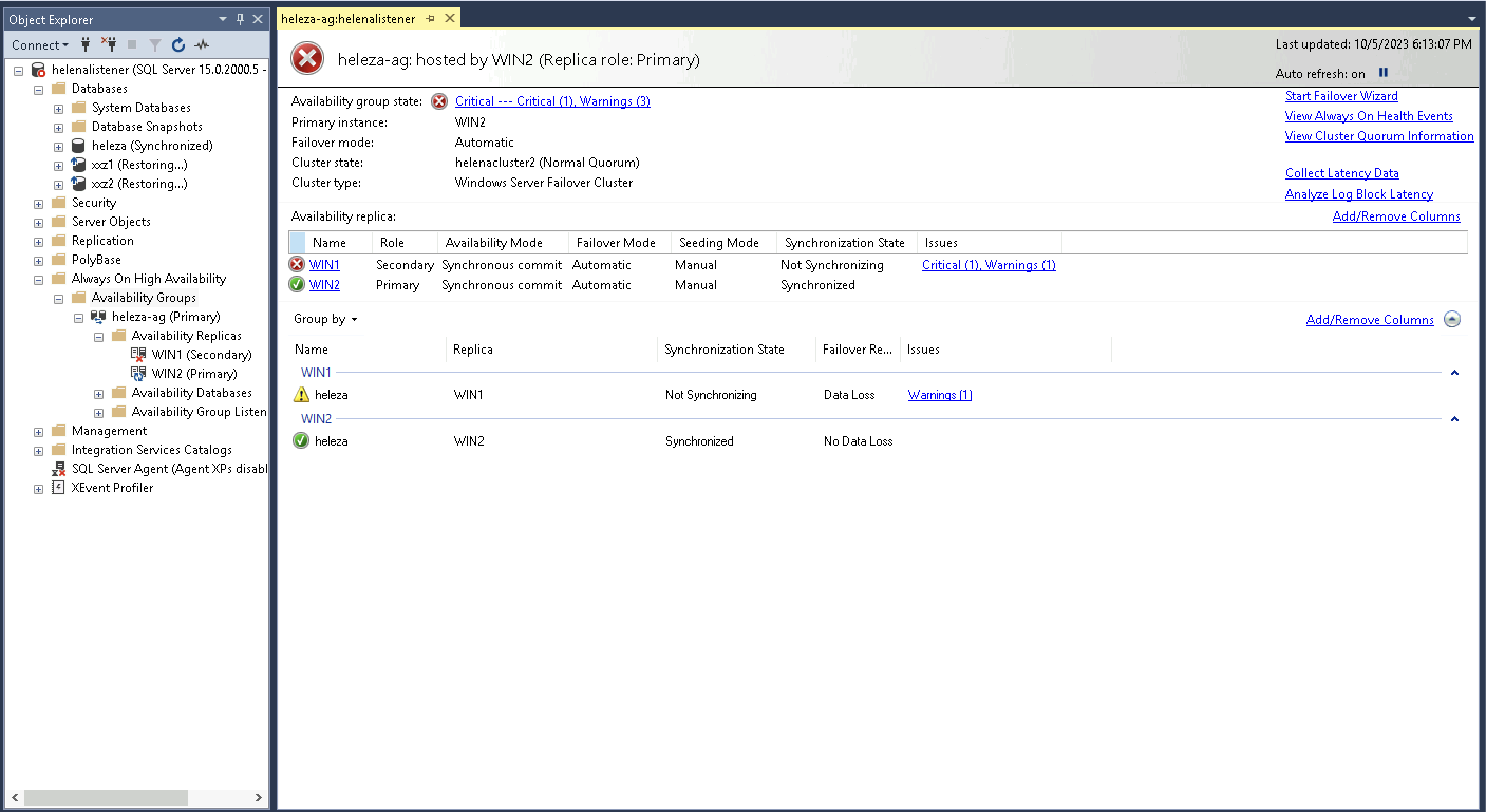
Opening the Always On Dashboard also shows the primary replica is now on Win2