VXLAN
VXLAN, or Virtual Extensible LAN, is a network virtualization technology that enables the creation of virtualized Layer 2 networks over an existing Layer 3 infrastructure. VXLAN overlays a Layer 2 network on top of a Layer 3 infrastructure, allowing for more flexible and scalable network design.
VXLAN Configuration
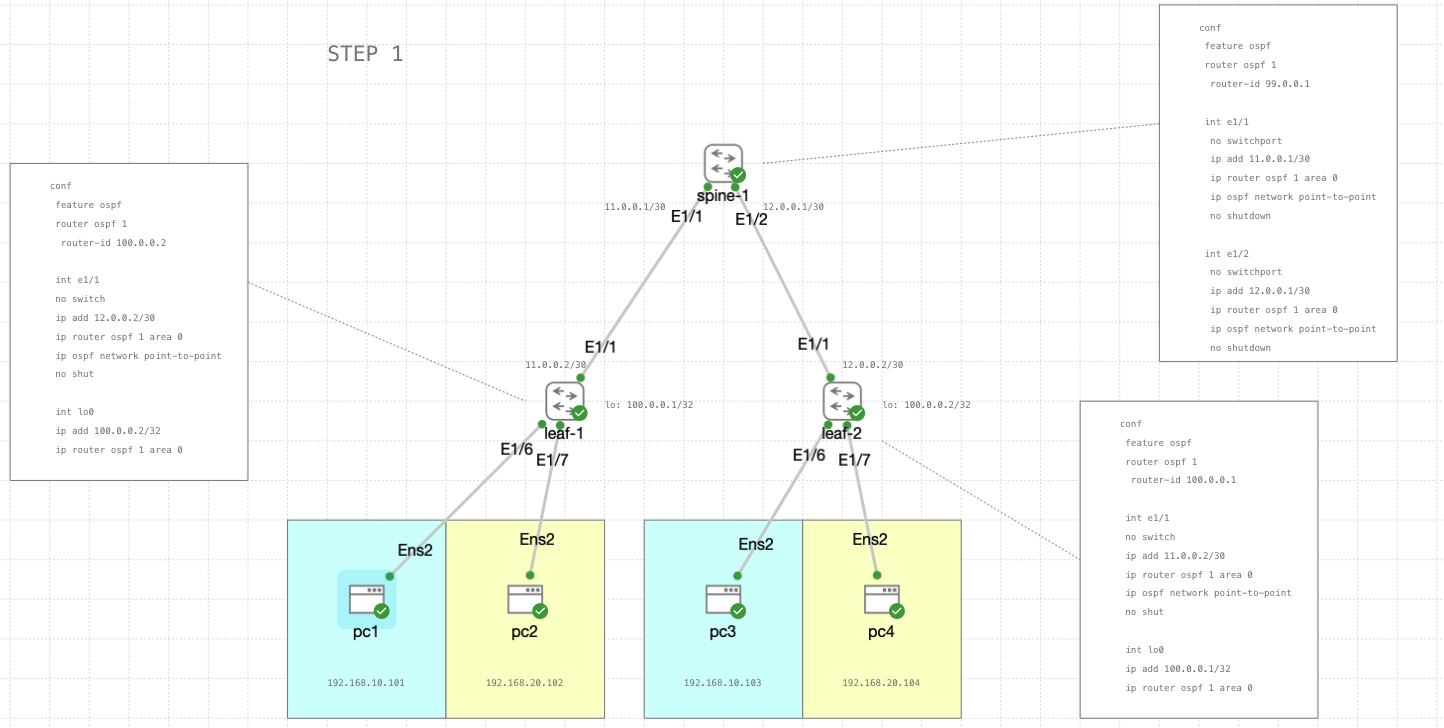
In this configuration we have 1 Spine and 2 Leaves, first we’ll configure the OSPF so all the siwtches can communicate properly to each other
spine-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
conf
feature ospf
router ospf 1
router-id 99.0.0.1
int e1/1
no switchport
ip add 11.0.0.1/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shutdown
int e1/2
no switchport
ip add 12.0.0.1/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shutdown
leaf-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
conf
feature ospf
router ospf 1
router-id 100.0.0.2
int e1/1
no switch
ip add 12.0.0.2/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shut
int lo0
ip add 100.0.0.2/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0
leaf-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
conf
feature ospf
router ospf 1
router-id 100.0.0.1
int e1/1
no switch
ip add 11.0.0.2/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shut
int lo0
ip add 100.0.0.1/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0
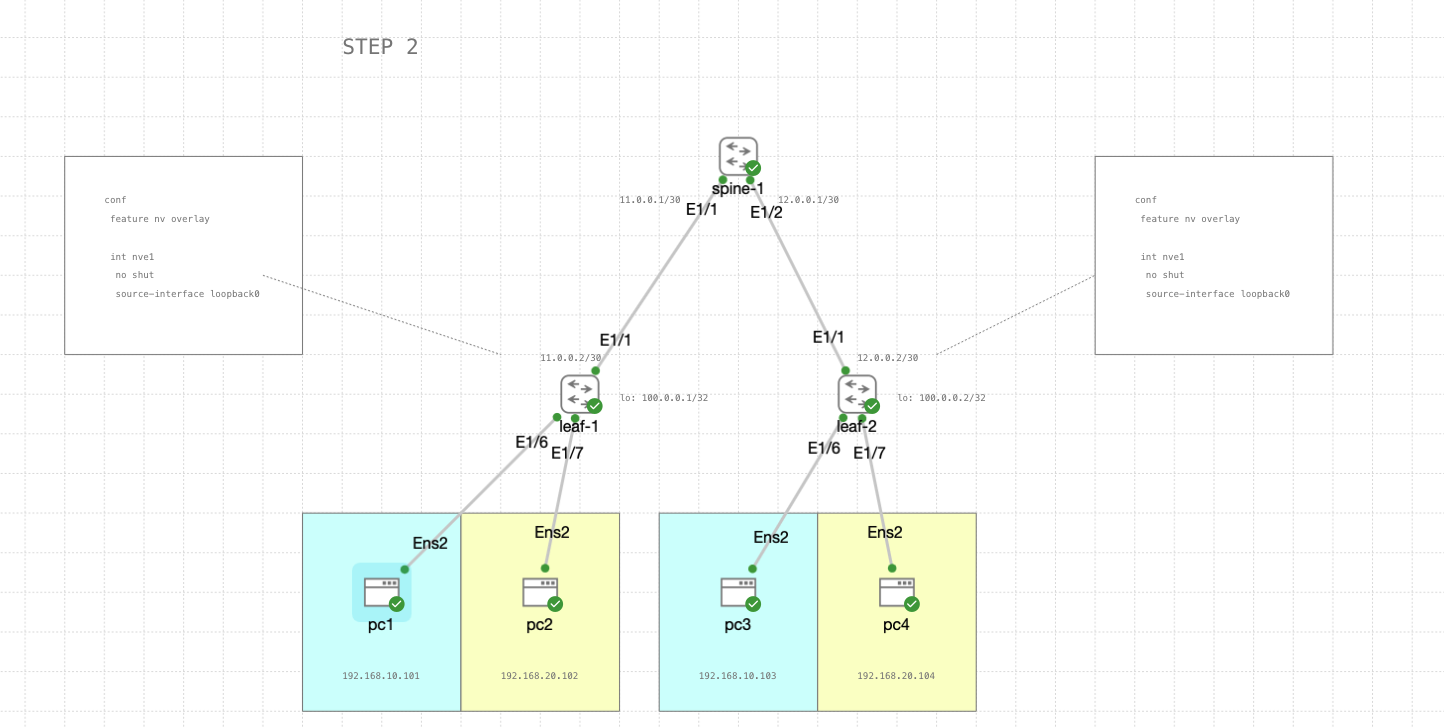
STEP 2
Next we configure the network virtualization overlay using the loopback interface
leaf-1 & leaf-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
conf
feature nv overlay
int nve1
no shut
source-interface loopback0
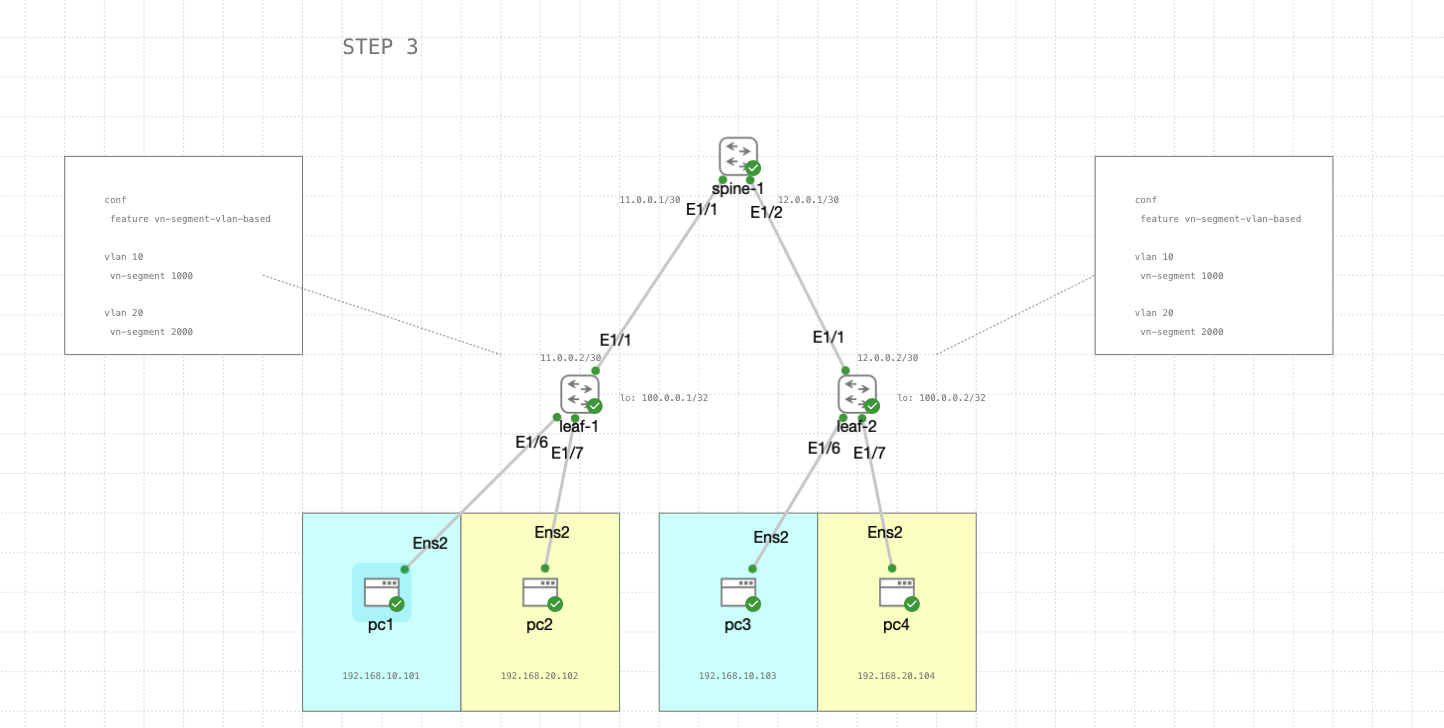
STEP 3
Next we enable VLAN-based segmentation for virtual networks, here each VLAN represents a separate segment of the network, and the vn-segment command assigns a unique identifier to each segment.
leaf-1 & leaf-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
conf
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
vlan 10
vn-segment 1000
vlan 20
vn-segment 2000
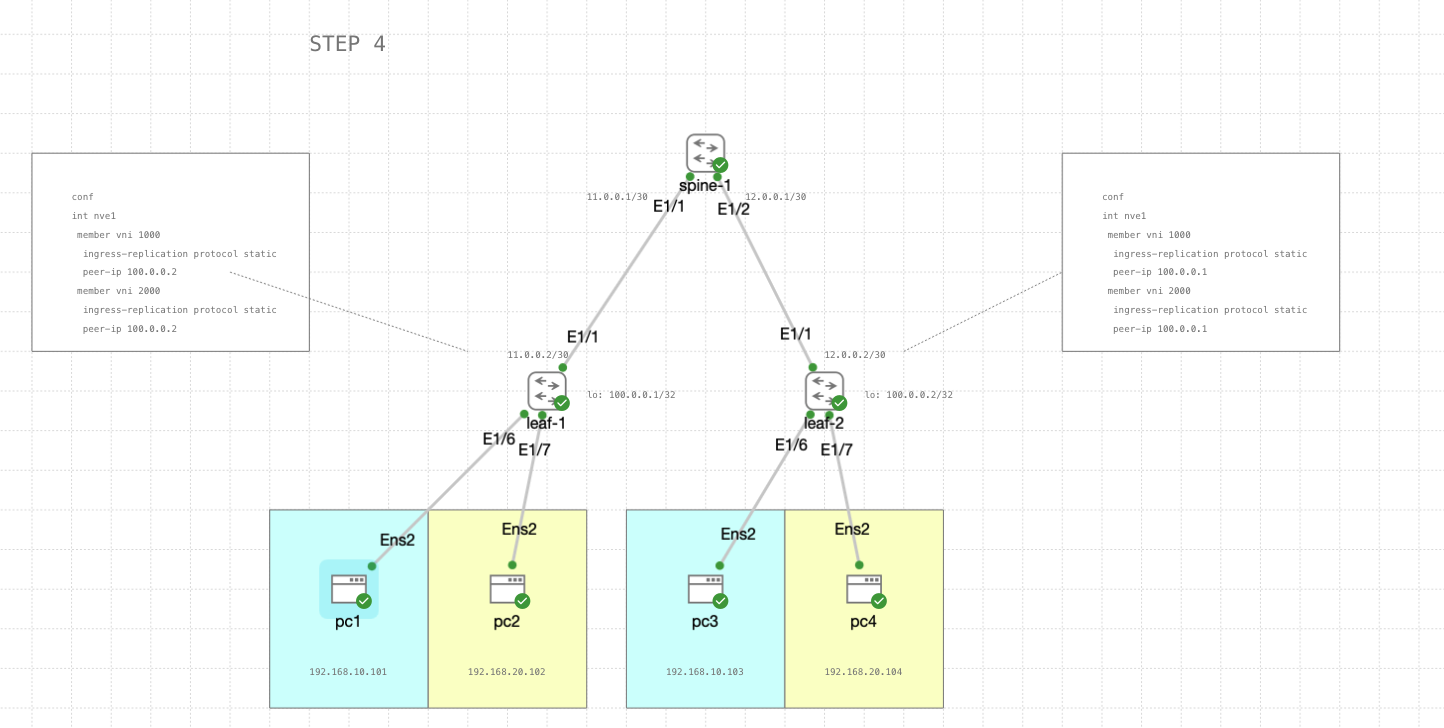
STEP 4
Next configuration is to set up the NVE (Network Virtualization Edge) interface nve1 with membership to two VNIs (Virtual Network Identifiers), namely VNI 1000 and VNI 2000.
In this configuration NVEs are used to encapsulate traffic from multiple VNIs and replicate it to peer devices for further distribution across the network. Each VNI represents a separate virtual network, and the NVE forwards traffic between the physical network and the virtual networks.
leaf-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
conf
int nve1
member vni 1000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.2
member vni 2000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.2
leaf-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
conf
int nve1
member vni 1000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.1
member vni 2000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.1
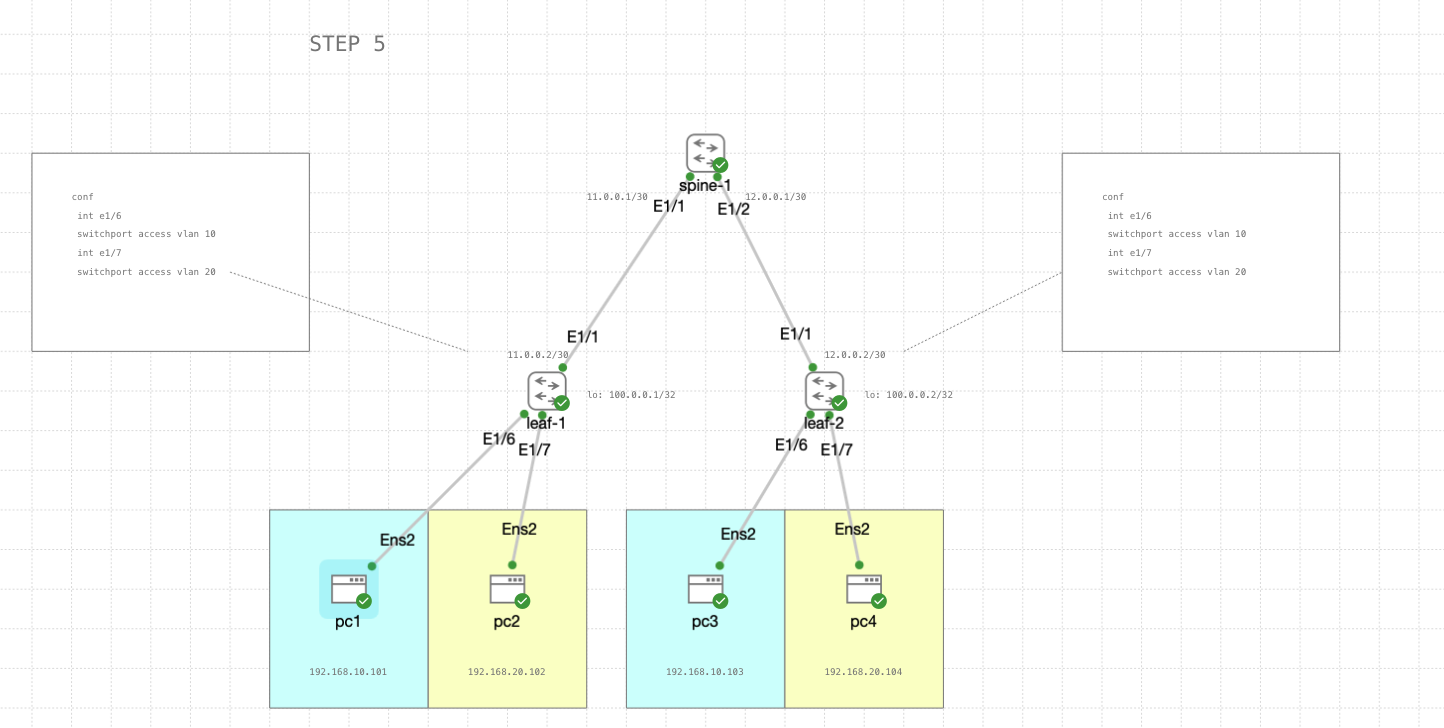
STEP 5
Lastly we set Ethernet1/6 and Ethernet1/7 as an access port to carry traffic for their respective VLAN
leaf-1 & leaf-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
conf
int e1/6
switchport access vlan 10
int e1/7
switchport access vlan 20
Testing VXLAN
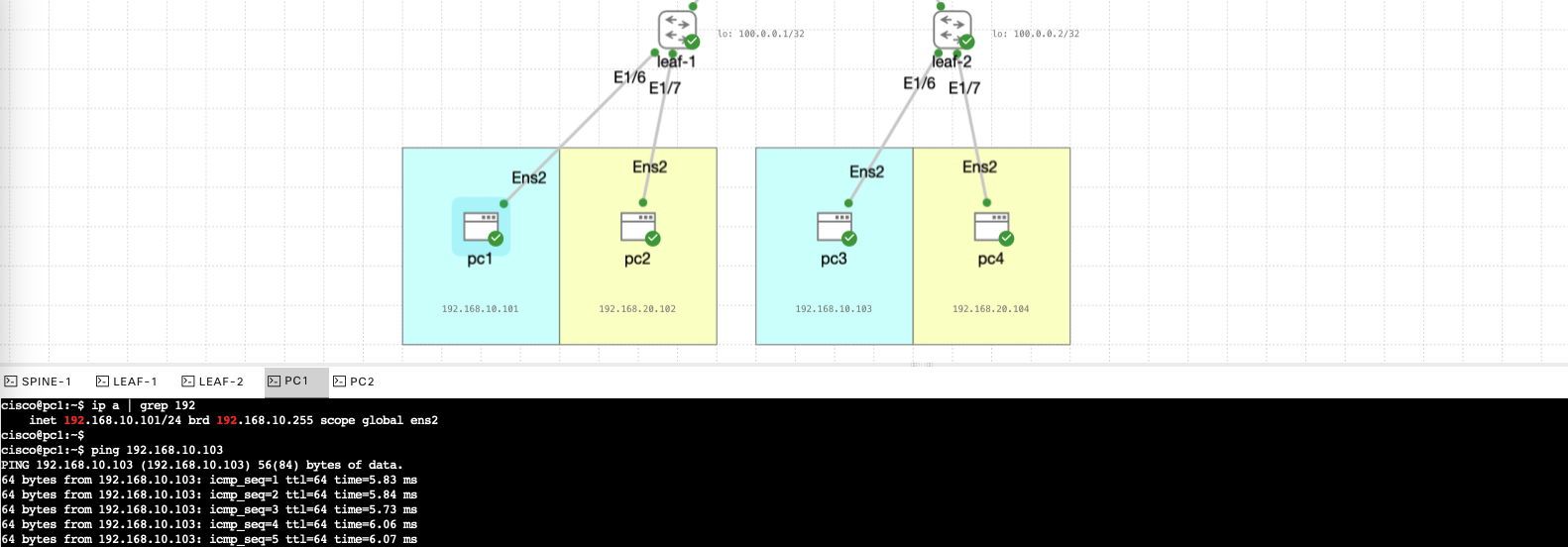
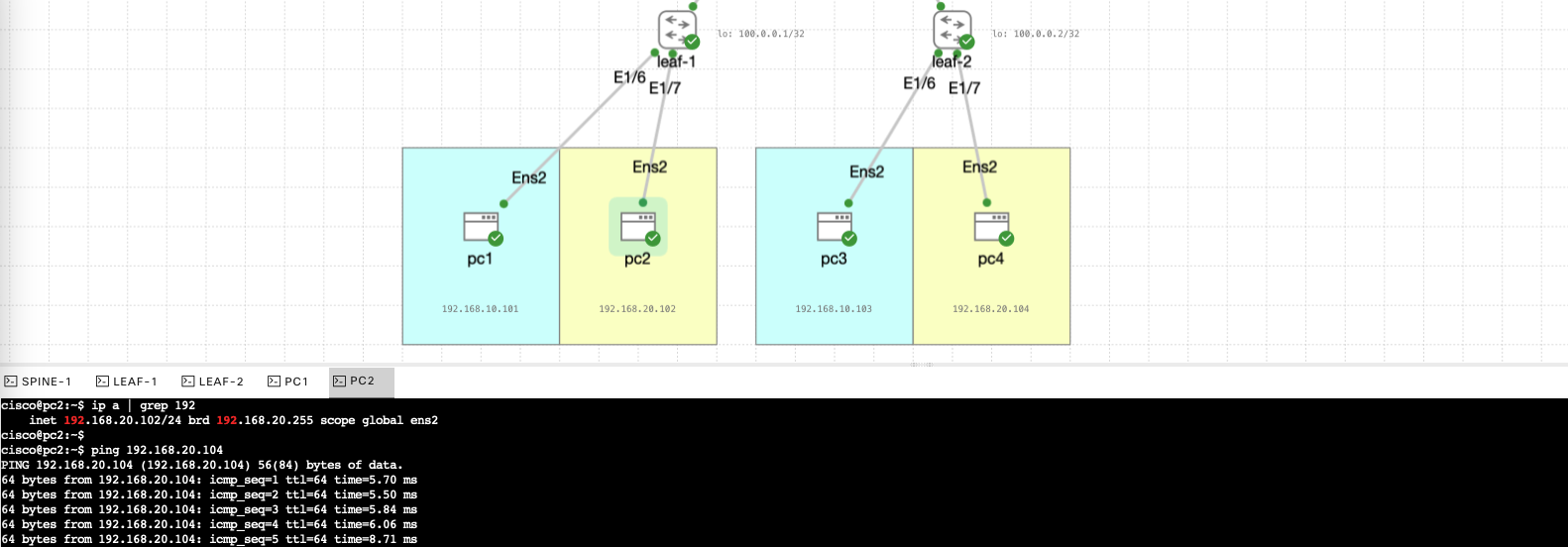
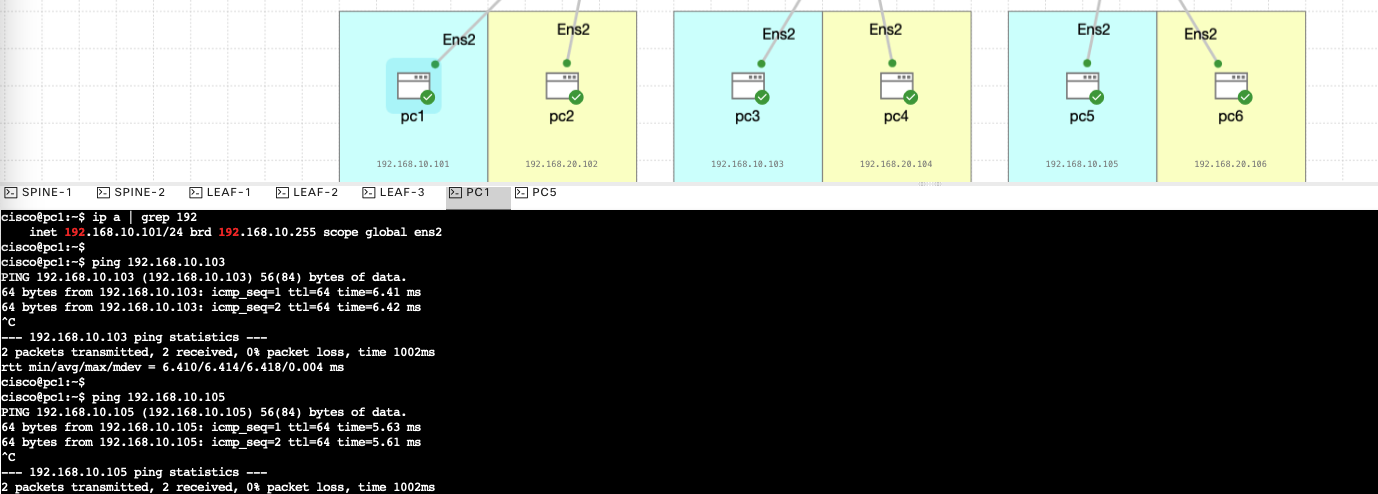
Now we test the connectivity between each leaf, wether in the same vlan or different vlan.
Here’ pc1 pinging pc3 successfully
And here’s pc1 pinging pc4 on different vlan also successfully
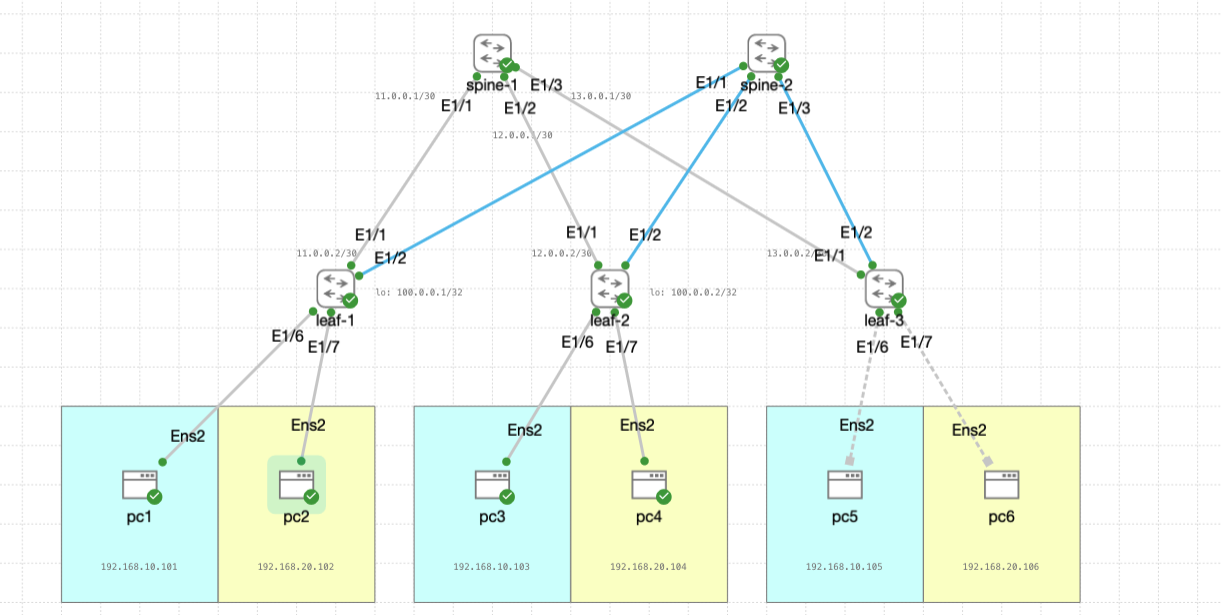
Scaling Up VXLAN
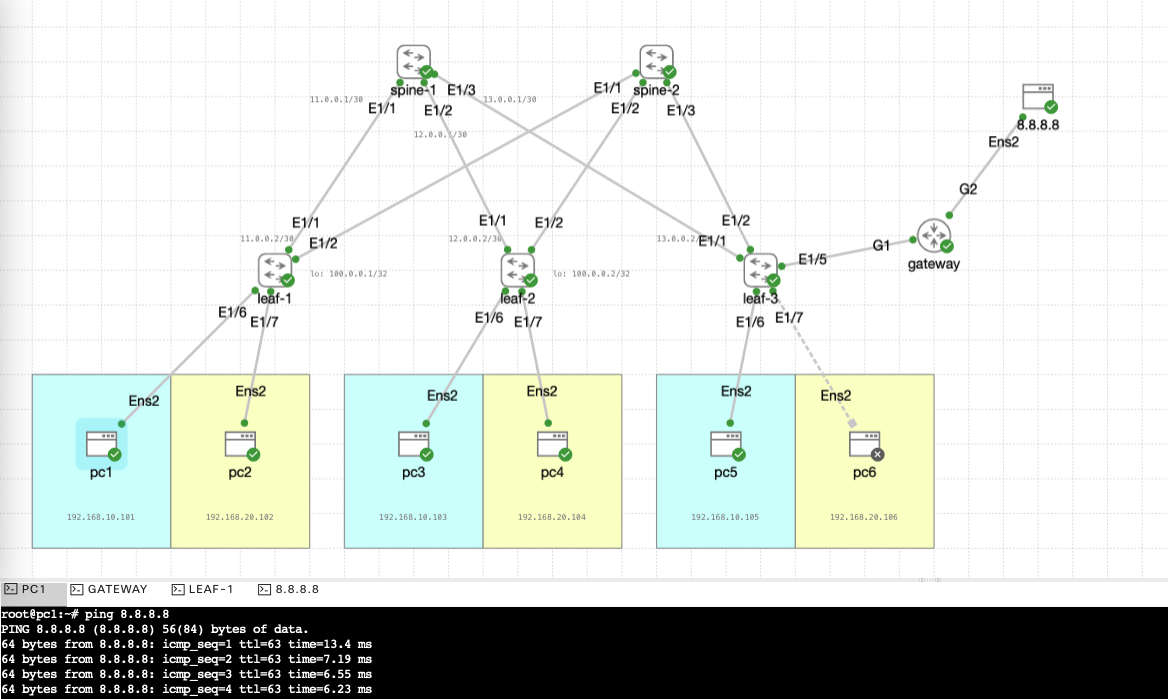
Next, we’ll scale up this topology by adding one more spine and leaf, so the configuration ends up like this
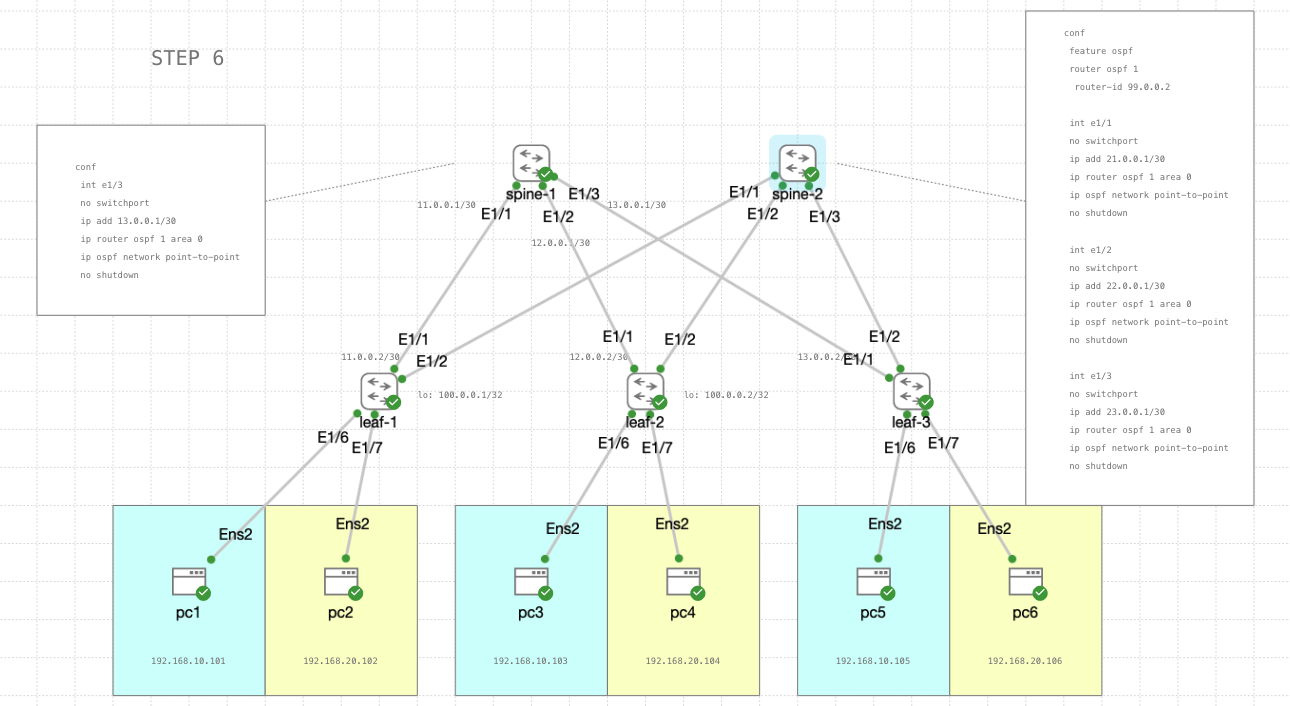
STEP 6
First lets configure OSPF to include the newly added switches on both spines
spine-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
conf
int e1/3
no switchport
ip add 13.0.0.1/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shutdown
spine-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
conf
feature ospf
router ospf 1
router-id 99.0.0.2
int e1/1
no switchport
ip add 21.0.0.1/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shutdown
int e1/2
no switchport
ip add 22.0.0.1/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shutdown
int e1/3
no switchport
ip add 23.0.0.1/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shutdown
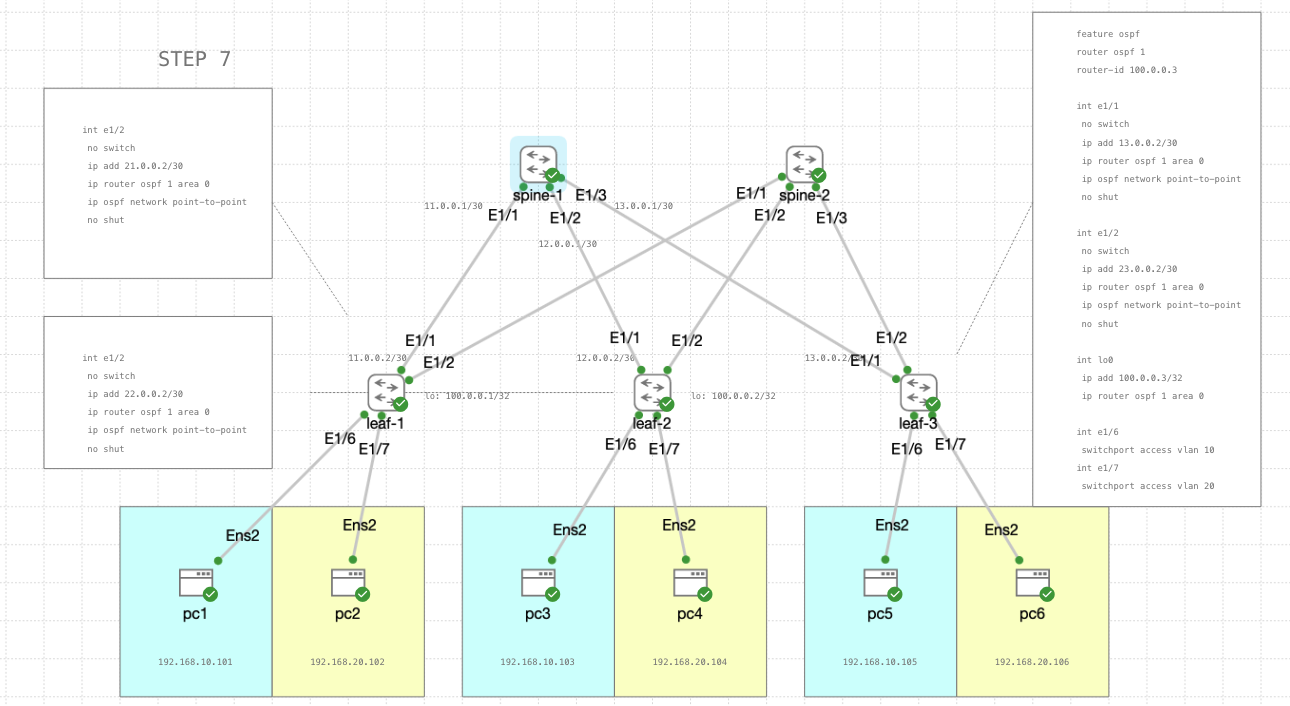
STEP 7
Continue the ospf configuration on leaf switches
leaf-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
conf
int e1/1
no switch
ip add 21.0.0.2/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shut
leaf-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
conf
int e1/1
no switch
ip add 22.0.0.2/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shut
leaf-3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
conf
feature ospf
router ospf 1
router-id 100.0.0.3
int e1/1
no switch
ip add 13.0.0.2/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shut
int e1/2
no switch
ip add 23.0.0.2/30
ip router ospf 1 area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
no shut
int lo0
ip add 100.0.0.3/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0
int e1/6
switchport access vlan 10
int e1/7
switchport access vlan 20
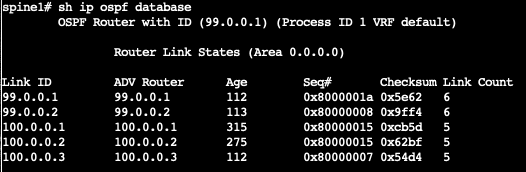
Taking a look at spine-1, we can see on its ospf database that all switches are now included in the ospf
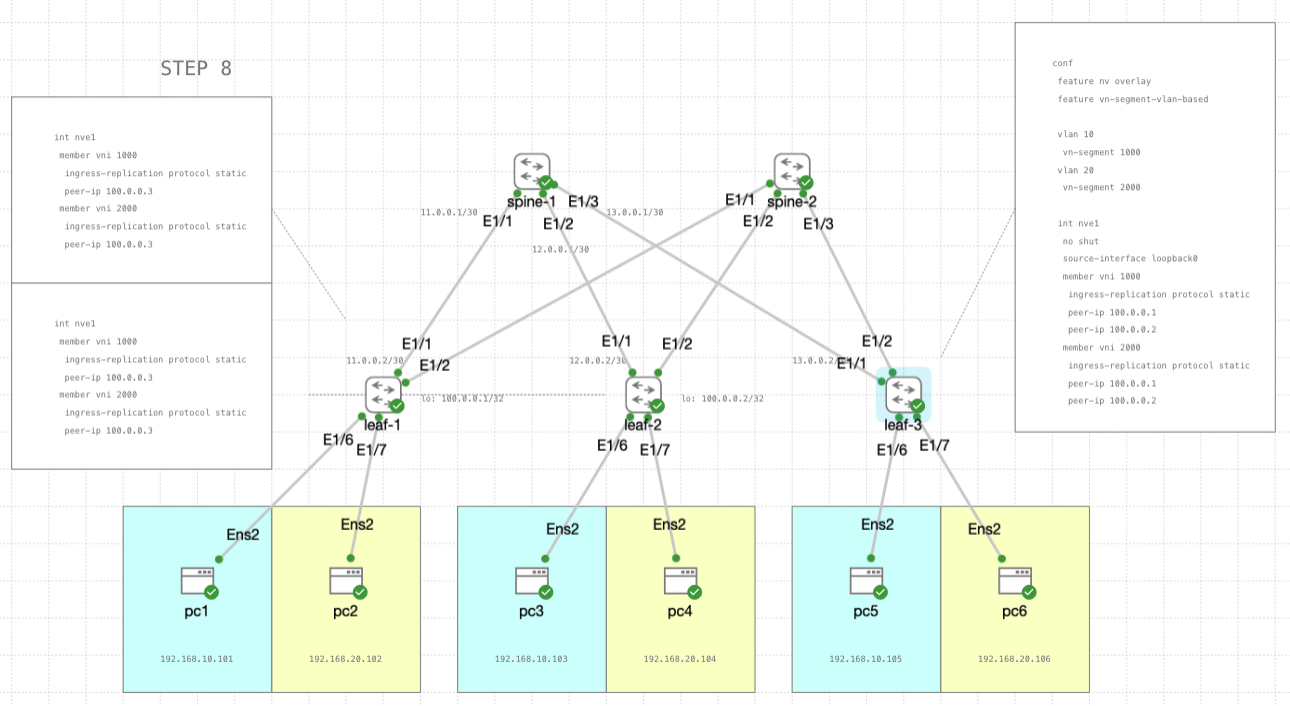
STEP 8
Lastly, now we configure the NVE interface to add leaf-3 as a peer
leaf-1 & leaf-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
conf
int nve1
member vni 1000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.3
member vni 2000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.3
leaf-3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
conf
feature nv overlay
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
vlan 10
vn-segment 1000
vlan 20
vn-segment 2000
int nve1
no shut
source-interface loopback0
member vni 1000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.1
peer-ip 100.0.0.2
member vni 2000
ingress-replication protocol static
peer-ip 100.0.0.1
peer-ip 100.0.0.2
Testing Scaled-up VXLAN
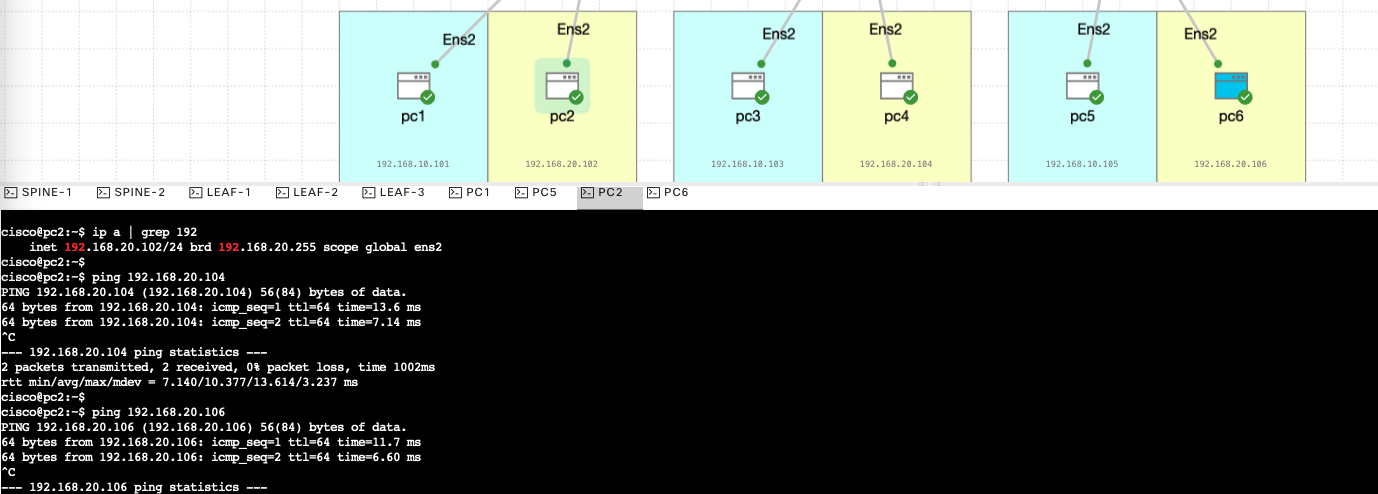
Now we try pinging from pc1 to pc3 and pc5
Same goes with pc2 to pc4 and pc6
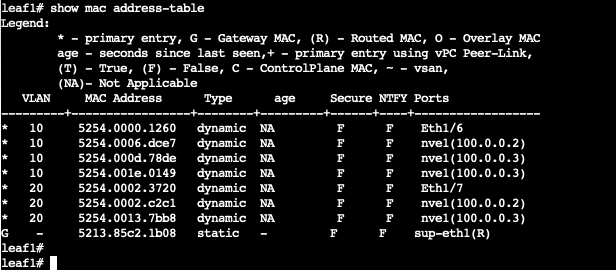
on a leaf switch, if we take a look at the mac address table, we can see that the leaf-1 learns mac address from 2 different ways, one is from its own interface and the other is from the nve interface
And lastly, if we want to have a layer3 out, we can add a gateway on any leaf for internet connection